13. Inventories¶
An Inventory is a collection of hosts against which jobs may be launched, the same as an Ansible inventory file. Inventories are divided into groups and these groups contain the actual hosts. Groups may be sourced manually, by entering host names into Tower, or from one of Ansible Tower’s supported cloud providers.
Note
If you have a custom dynamic inventory script, or a cloud provider that is not yet supported natively in Tower, you can also import that into Tower. Refer to the Tower Administration Guide.
This tab displays a list of the inventories that are currently available. The inventory list may be sorted and searched by Name, Type, or Organization.
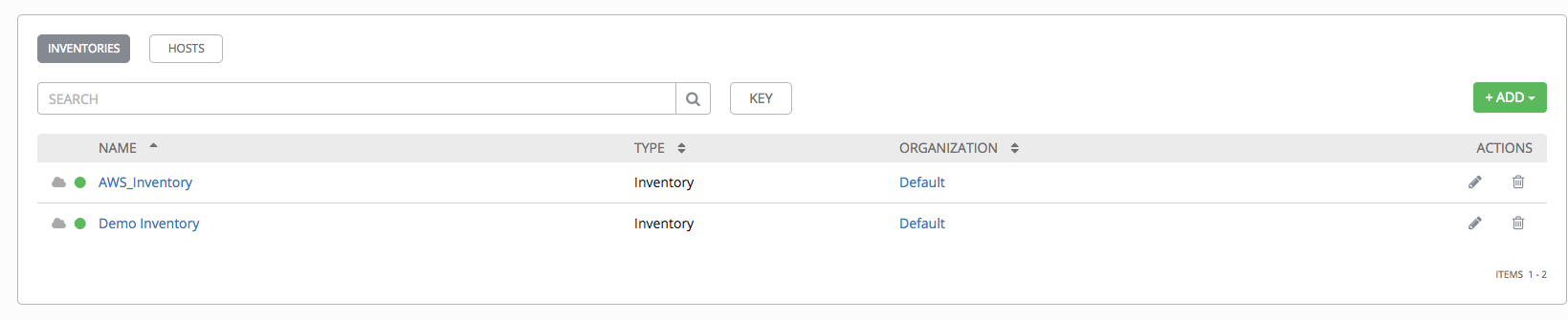
The list of Inventory details includes:
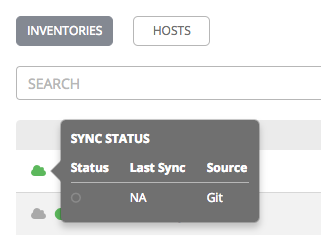
- Inventory Sync (
 ): Green indicates successful syncs in the inventory, and red indicates failed syncs. Clicking this icon displays the sync status for the last five inventory source syncs and source information, if the inventory has sources that are able to sync.
): Green indicates successful syncs in the inventory, and red indicates failed syncs. Clicking this icon displays the sync status for the last five inventory source syncs and source information, if the inventory has sources that are able to sync.
- Status Dot: This shows the status of recent jobs for this inventory.
- Name: The inventory name. Clicking the Inventory name navigates to the properties screen for the selected inventory, which shows the inventory’s groups and hosts. (This view is also accessible from the
 icon.)
icon.)
Type: Identifies whether it is a standard inventory or a Smart Inventory.
Organization: The organization to which the inventory belongs.
Actions: The following actions are available for the selected inventory:
- Edit: Edit the properties for the selected inventory
- Delete: Delete the selected inventory. This operation cannot be reversed!
13.1. Smart Inventories¶
A Smart Inventory is a collection of hosts defined by a stored search that can be viewed like a standard inventory and made to be easily used with job runs. Organization administrators have admin permission to inventories in their organization and can create Smart Inventories. A Smart Inventory is identified by KIND=smart. You can define a Smart Inventory using the same method being used with Tower Search. InventorySource is directly associated with an Inventory.
The Inventory model has the following new fields that are blank by default but are set accordingly for Smart Inventories:
kindis set tosmartfor Smart Inventorieshost_filteris set ANDkindis set tosmartfor Smart Inventories.
The host model has a new field, smart_inventories that uses a membership lookup table that identifies a set of all the Smart Inventory a host is associated with. The memberships are generated by a task. The task is launched when:
- a new host is added
- an existing host is modified (updated or deleted)
- a new Smart Inventory is added
- an existing Smart Inventory is modified (updated or deleted)
Note
The update_host_smart_inventory_memberships task is only run if the AWX_REBUILD_SMART_MEMBERSHIP is set to True (default is False).
You can view actual inventories without being editable:
- Names of Host and Group created as a result of an inventory source sync
- Group records cannot be edited or moved
You cannot create hosts from a Smart Inventory host endpoint (/inventories/N/hosts/) as with a normal inventory. The administrator of a Smart Inventory has permission to edit fields such as the name, description, variables, and the ability to delete, but does not have the permission to modify the host_filter, because that will affect which hosts (that have a primary membership inside another inventory) are included in the smart inventory. Note, host_filter only apply to hosts inside of inventories inside of the Smart Inventory’s organization.
In order to modify the host_filter, you need to be the organization administrator of the inventory’s organization. Organization admins already have implicit “admin” access to all inventories inside the organization, therefore, this does not convey any permissions they did not already possess.
Administrators of the Smart Inventory can grant other users (who are not also admins of your organization) permissions like “use” “adhoc” to the smart inventory, and these will allow the actions indicate by the role, just like other standard inventories. However, this will not give them any special permissions to hosts (which live in a different inventory). It will not allow them direct read permission to hosts, or permit them to see additional hosts under /#/hosts/, although they can still view the hosts under the smart inventory host list.
In some situations, you can modify the following:
- A new Host manually created on Inventory w/ inventory sources
- In Groups that were created as a result of inventory source syncs
- Variables on Host and Group are changeable
Hosts associated with the Smart Inventory are manifested at view time. If the results of a Smart Inventory contains more than one host with identical hostnames, only one of the matching hosts will be included as part of the Smart Inventory, ordered by Host ID.
13.1.1. host_filter Search¶
You can search host_filter by host name, group name, and Ansible facts.
The format for a group search is:
groups.name:groupA
The format for a fact search is:
ansible_facts.ansible_fips:false
You can also perform Smart Search searches, which consist a host name and host description.
host_filter=name=my_host
If a search term in host_filter is of string type, to make the value a number (e.g. 2.66), or a JSON keyword (e.g. null, true or false) valid, add double quotations around the value to prevent Tower from mistakenly parsing it as a non-string:
host_filter=ansible_facts__packages__dnsmasq[]__version="2.66"
13.2. Add a new inventory¶
To create a new inventory or Smart Inventory:
- Click the
 button, and select the type of inventory to create.
button, and select the type of inventory to create.
The type of inventory is identified by the labels and the row of tabs across the top of the create form.
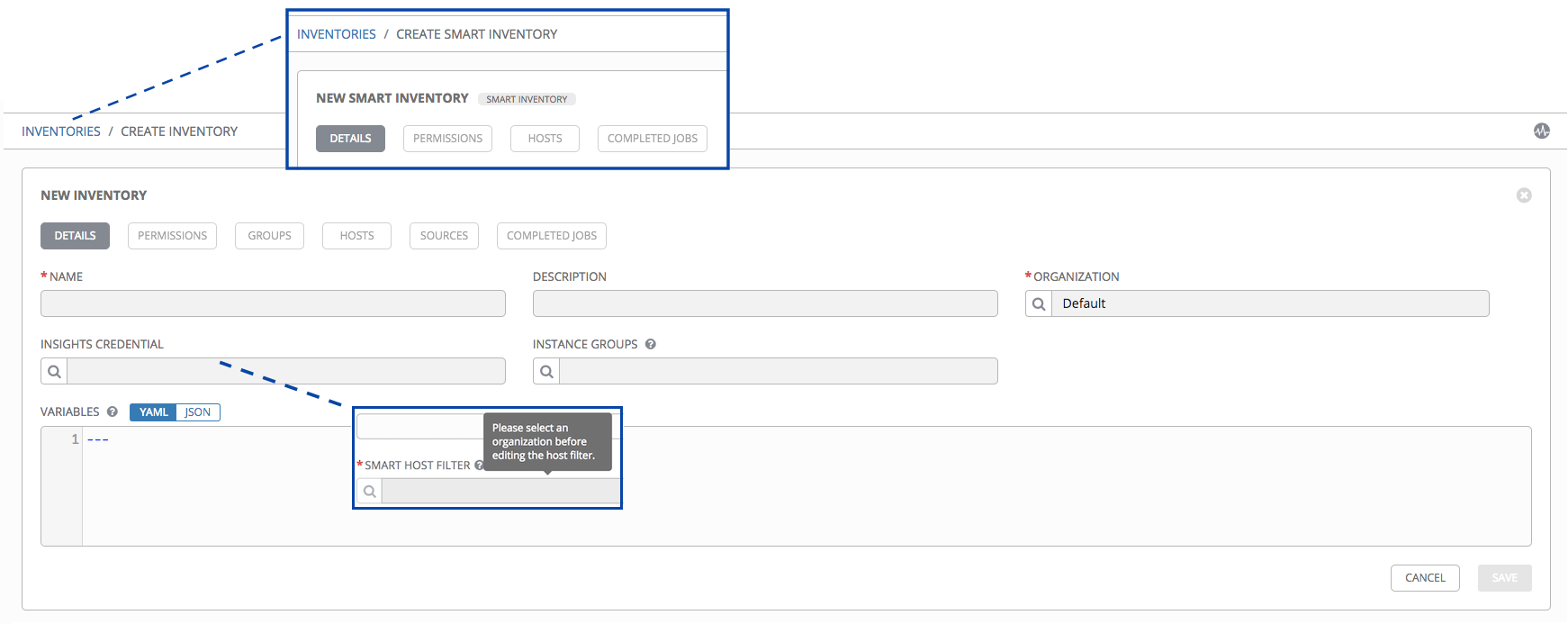
- Enter the appropriate details into the following fields:
Name: Enter a name appropriate for this inventory.
Description: Enter an arbitrary description as appropriate (optional).
Organization: Required. Choose among the available organizations.
Smart Host Filter: (Only applicable to Smart Inventories) Click the
 button to open a separate Dynamic Hosts window to filter hosts for this inventory. These options are based on the organization you chose.
button to open a separate Dynamic Hosts window to filter hosts for this inventory. These options are based on the organization you chose.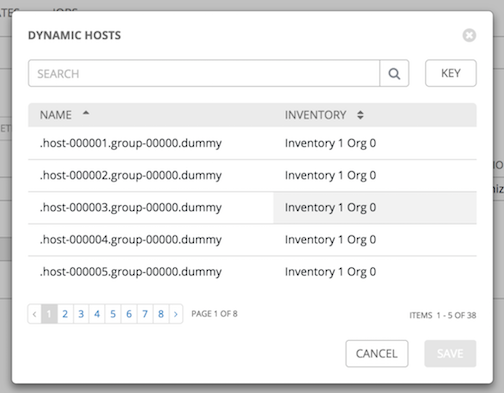
Filters are similar to tags in that tags are used to filter certain hosts that contain those names. Filters are case-sensitive. Refer to the Smart Host Filter section for more information.
Insights Credential: (Only applicable to standard inventories) Enter the appropriate Insights credential if the inventory is used with Insights.
Instance Groups: Click the
 button to open a separate window. Choose the instance groups for this inventory to run on. If the list is extensive, use the search to narrow the options.
button to open a separate window. Choose the instance groups for this inventory to run on. If the list is extensive, use the search to narrow the options.Variables: Variable definitions and values to be applied to all hosts in this inventory. Enter variables using either JSON or YAML syntax. Use the radio button to toggle between the two.
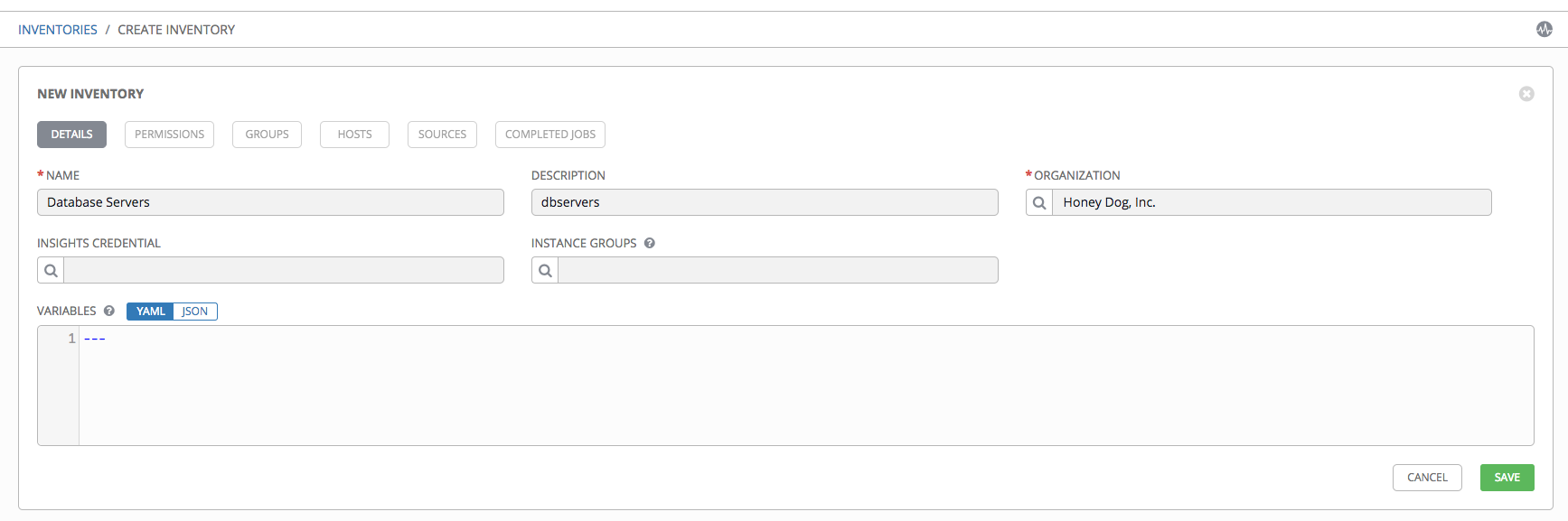
- Click Save when done.
After Tower saves the new inventory, you can proceed with configuring permissions, groups, hosts, sources, and view completed jobs, if applicable to the type of inventory. For more instructions, refer to the subsequent sections.
13.2.1. Add Permissions¶
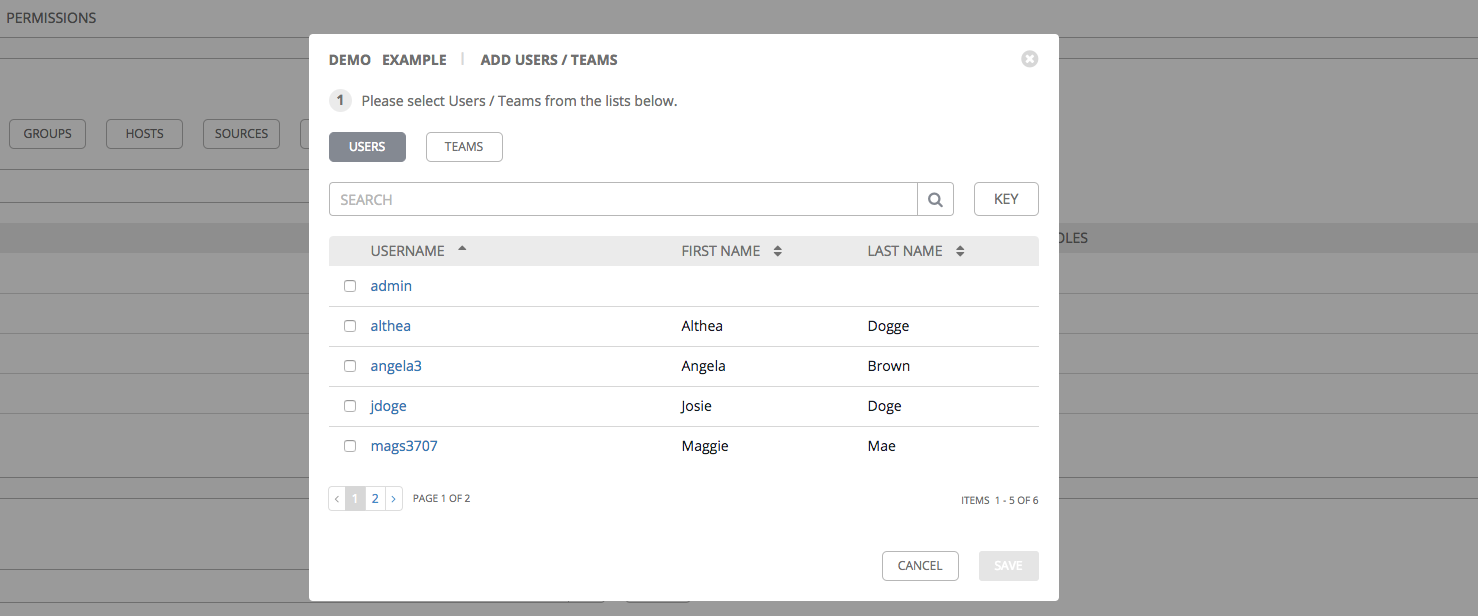
The Permissions tab allows you to review, grant, edit, and remove associated permissions for users as well as team members. To assign permissions to a particular user for this resource:
- Click the Permissions tab.
- Click the
 button to open the Add Users/Teams window.
button to open the Add Users/Teams window.
- Specify the users or teams that will have access then assign them specific roles:
- Click to select one or multiple checkboxes beside the name(s) of the user(s) or team(s) to select them.
Note
You can select multiple users and teams at the same time by navigating between the Users and Teams tabs without saving.
After selections are made, the window expands to allow you to select a role from the drop-down menu list for each user or team you chose.
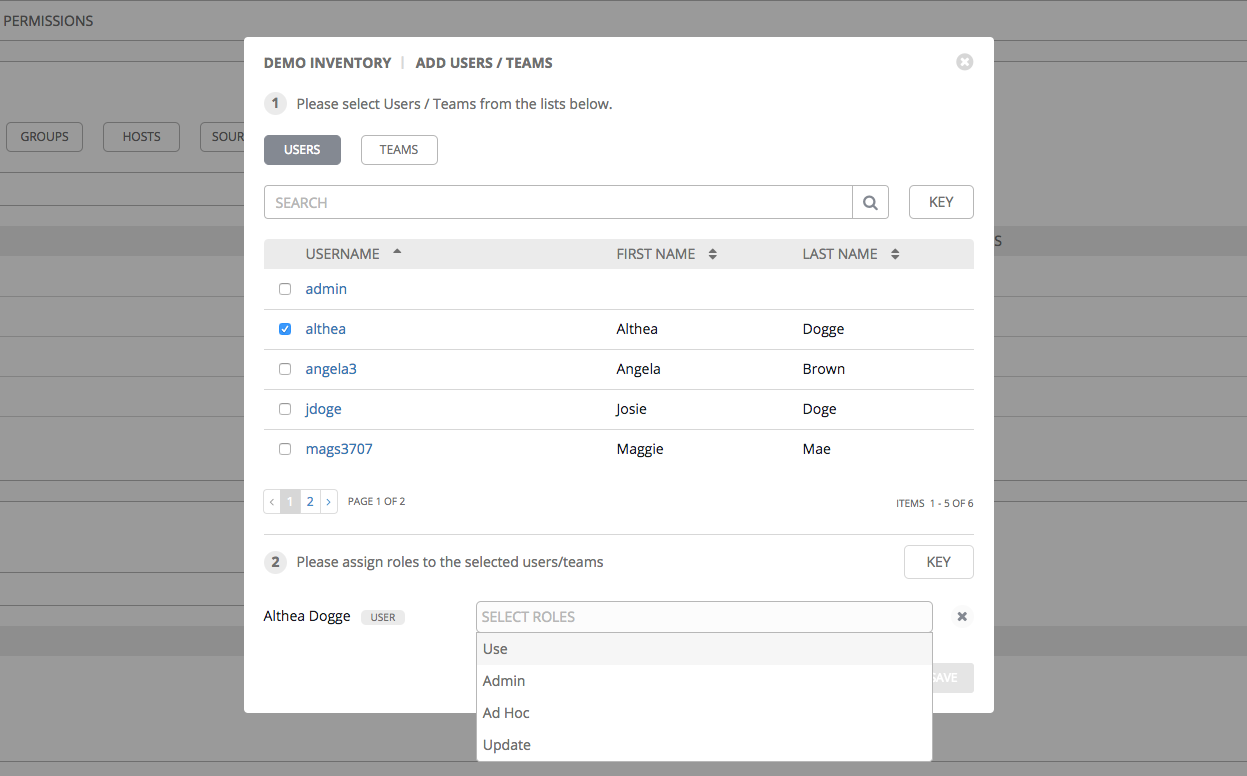
The example above shows options associated with inventories. Different resources have different options available:
- Admin allows read, run, and edit privileges (applies to all resources)
- Use allows use of a resource in a job template (applies all resources except job templates)
- Update allows updating of project via the SCM Update (applies to projects and inventories)
- Ad Hoc allows use of Ad Hoc commands (applies to inventories)
- Execute allows launching of a job template (applies to job templates)
Tip
Use the Key button in the roles selection pane to display a description of each of the roles.
- Select the role to apply to the selected user or team.
Note
You can assign roles to multiple users and teams by navigating between the Users and Teams tabs without saving.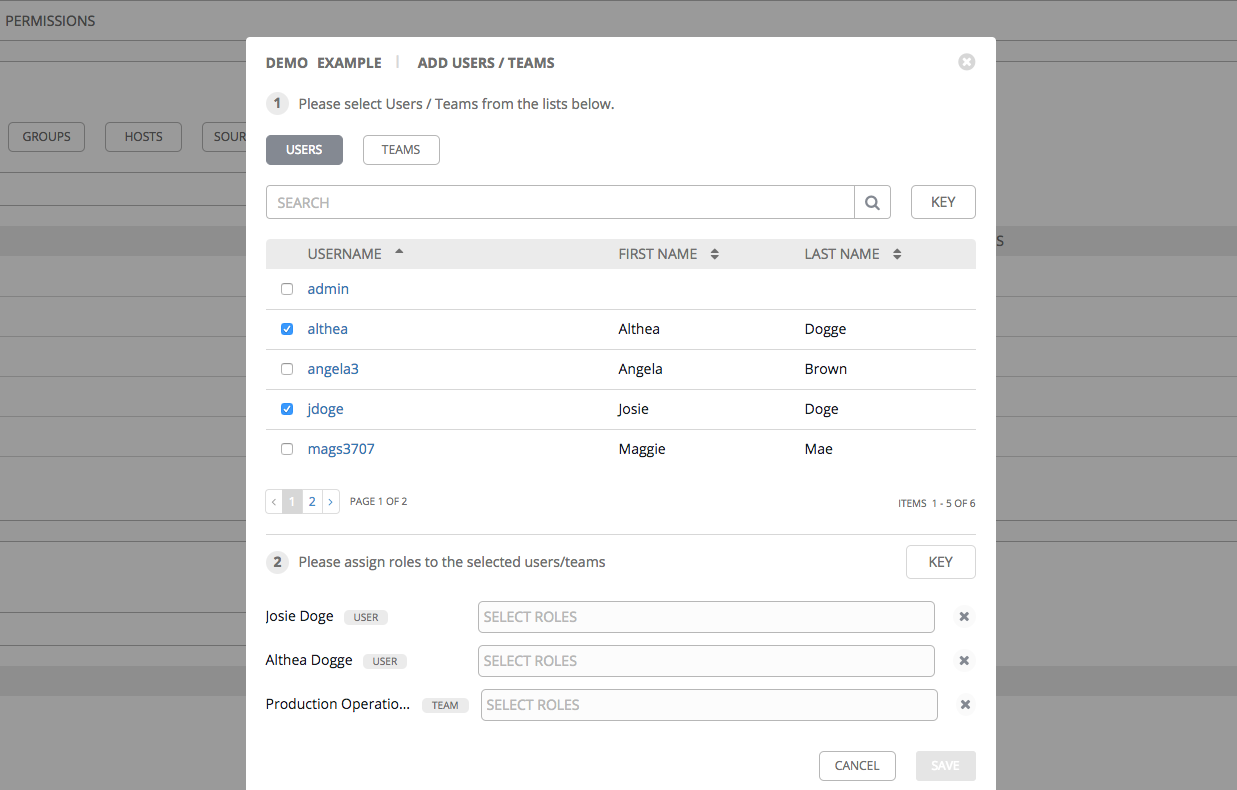
- Review your role assignments for each user and team.
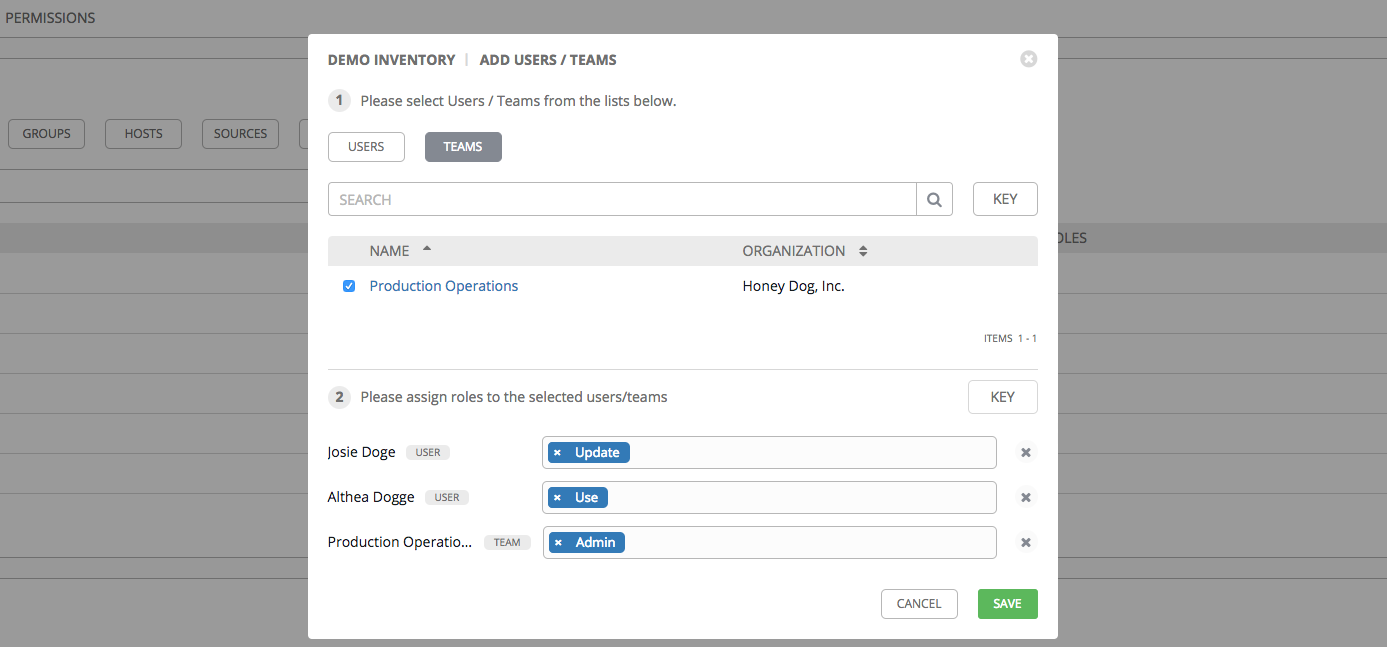
Click Save when done, and the Add Users/Teams window closes to display the updated roles assigned for each user and team.
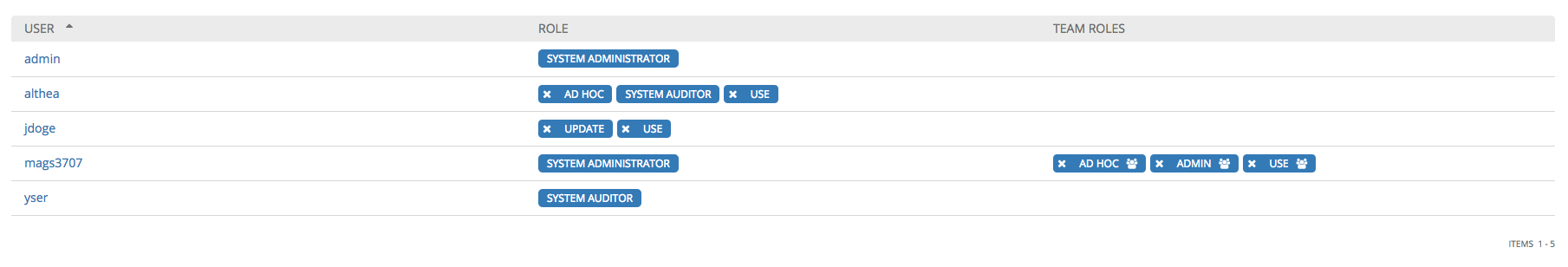
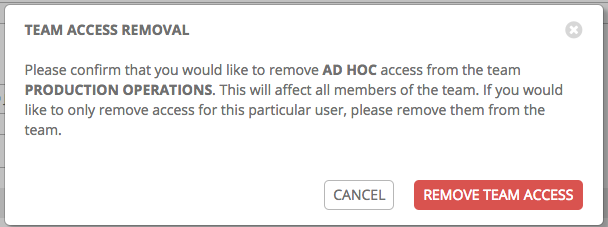
To remove Permissions for a particular user, click the Disassociate (x) button next to its resource.
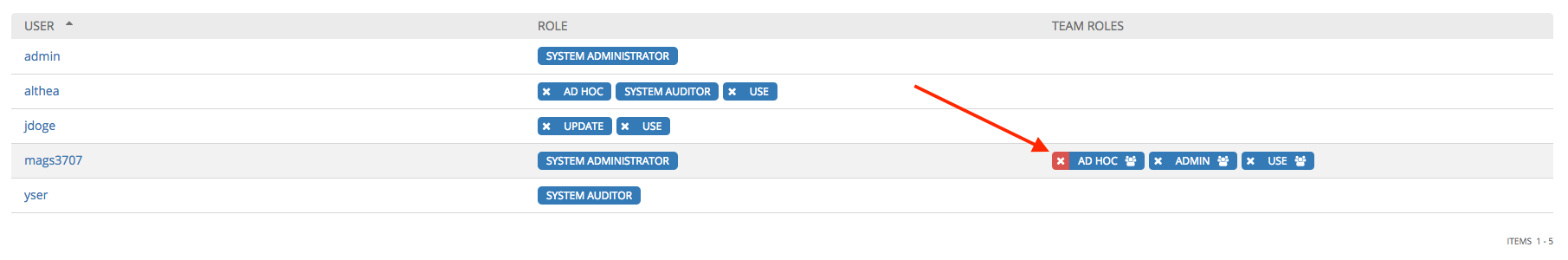
This launches a confirmation dialog, asking you to confirm the disassociation.
13.2.2. Add Groups¶
Inventories are divided into groups, which may contain hosts and other groups, and hosts. Groups are only applicable to standard inventories and is not a configurable directly through a Smart Inventory. You can associate an existing group through host(s) that are used with standard inventories. There are several actions available for standard inventories:
- Create a new Group
- Create a new Host
- Run a command on the selected Inventory
- Edit Inventory properties
- View activity streams for Groups and Hosts
- Obtain help building your Inventory
Note
Starting in Ansible Tower 3.2, inventory sources are no longer associated with groups. Prior versions, spawned groups and hosts would be children of our inventory source group. Now, spawned groups are top-level. These groups may still have child groups, and all of these spawned groups may have hosts.
To create a new group for an inventory:
- Click the
 button to open the Create Group window.
button to open the Create Group window.
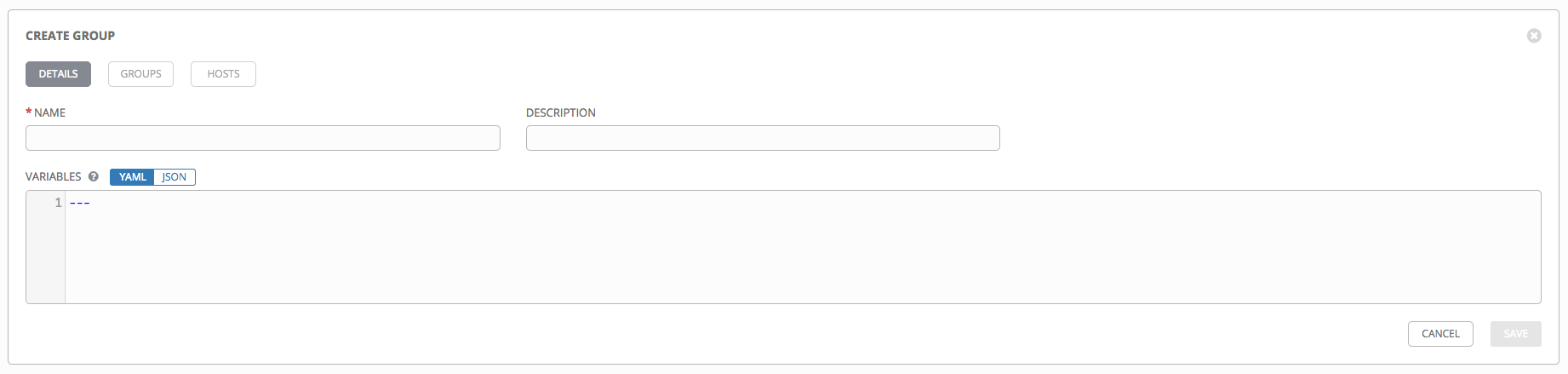
- Enter the appropriate details into the required and optional fields:
- Name: Required
- Description: Enter an arbitrary description as appropriate (optional)
- Variables: Enter definitions and values to be applied to all hosts in this group. Enter variables using either JSON or YAML syntax. Use the radio button to toggle between the two.
- When done, click Save.
13.2.2.1. Add groups within groups¶
To add groups within groups:
- Click the Groups tab.
- Click the
 button, and select whether to add a group that already exists in your configuration or create a new group.
button, and select whether to add a group that already exists in your configuration or create a new group.
- If creating a new group, enter the appropriate details into the required and optional fields:
- Name: Required
- Description: Enter an arbitrary description as appropriate (optional)
- Variables: Enter definitions and values to be applied to all hosts in this group. Enter variables using either JSON or YAML syntax. Use the radio button to toggle between the two.
- When done, click Save.
The Create Group window closes and the newly created group displays as an entry in the list of groups associated with the group that it was created for.
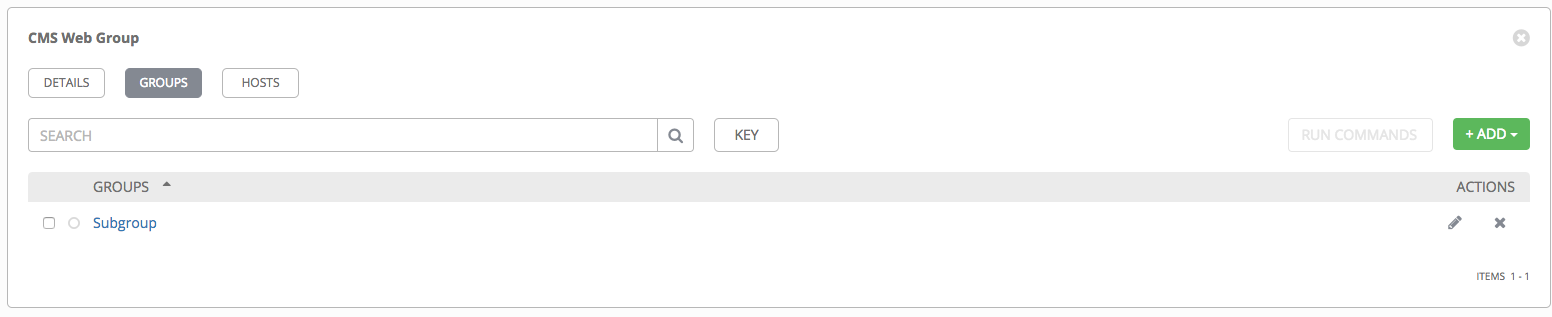
If you chose to add an existing group, available groups will appear in a separate selection window.
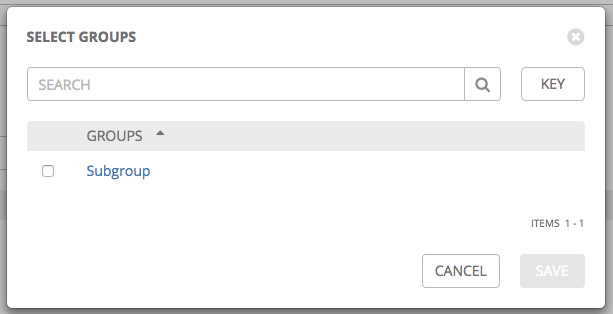
Once a group is selected, it displays as an entry in the list of groups associated with the group.
5. To configure additional groups and hosts under the subgroup, click on the name of the subgroup from the list of groups and repeat the same steps described in this section.
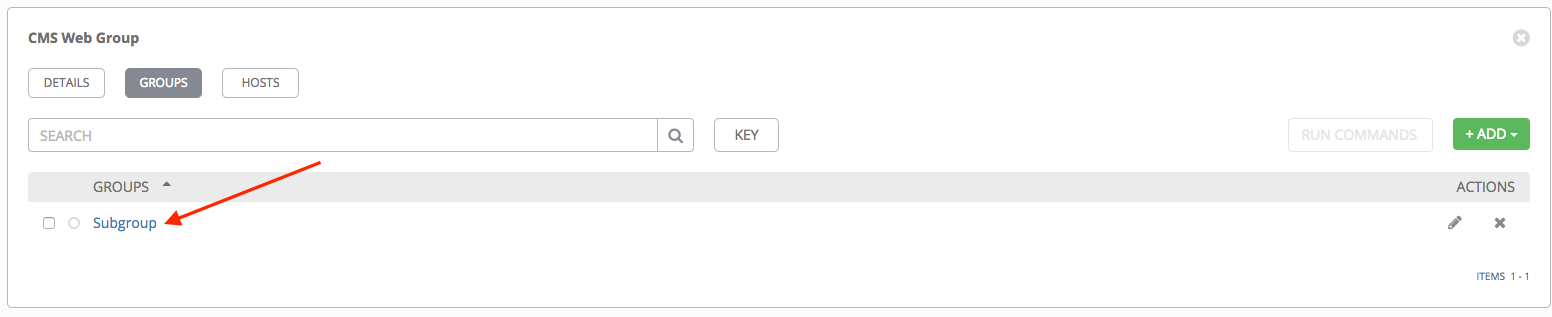
13.2.3. Add hosts¶
You can configure hosts for the inventory as well as for groups and groups within groups. To configure hosts:
- Click the Hosts tab.
- Click the
 button, and select whether to add a host that already exists in your configuration or create a new host.
button, and select whether to add a host that already exists in your configuration or create a new host.
- If creating a new host, select the
 button to specify whether or not to include this host while running jobs.
button to specify whether or not to include this host while running jobs.
- Enter the appropriate details into the required and optional fields:
- Host Name: Required
- Description: Enter an arbitrary description as appropriate (optional)
- Variables: Enter definitions and values to be applied to all hosts in this group. Enter variables using either JSON or YAML syntax. Use the radio button to toggle between the two.
- When done, click Save.
The Create Host window closes and the newly created host displays as an entry in the list of hosts associated with the group that it was created for.
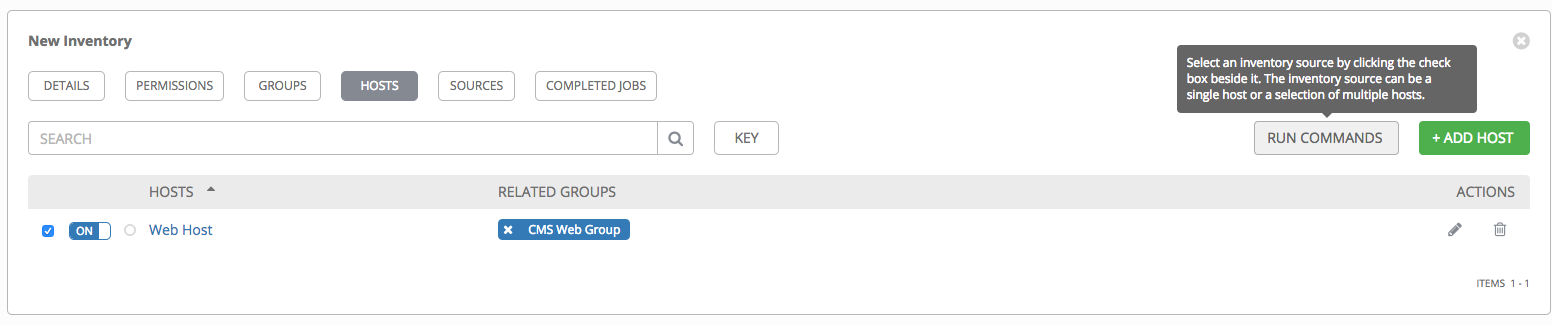
If you chose to add an existing host, available hosts will appear in a separate selection window.
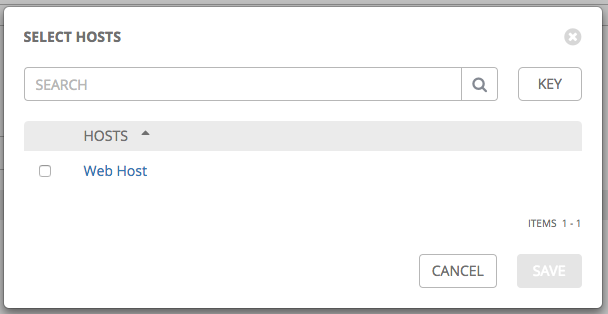
Once a host is selected, it displays as an entry in the list of hosts associated with the group.
6. To configure facts and additional groups for the host, click on the name of the host from the list of hosts.
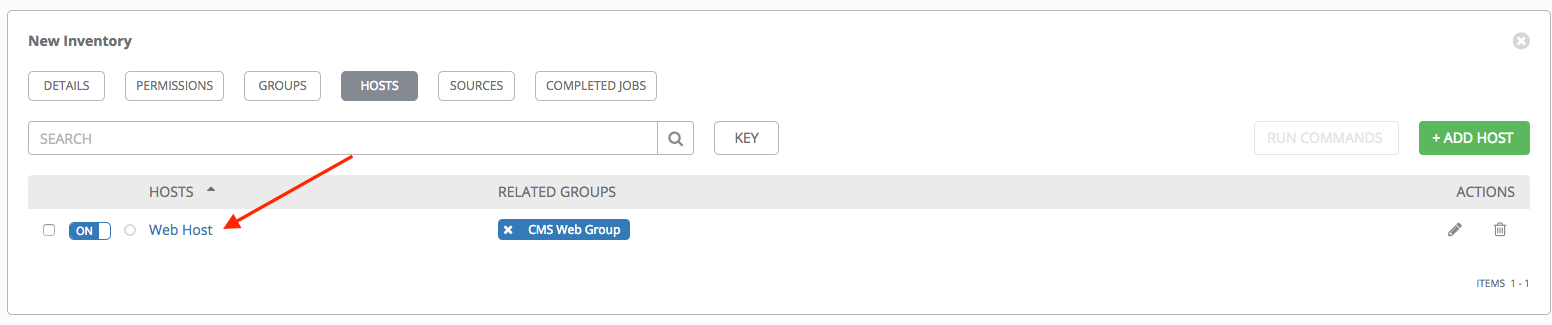
This opens the Details tab of the selected host.
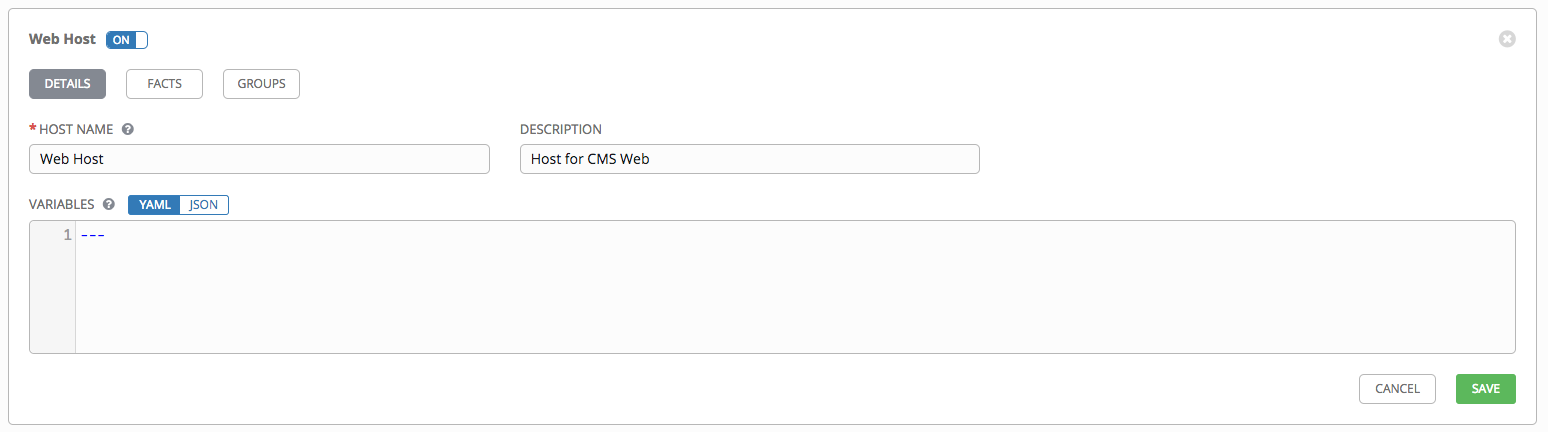
- Click the Facts tab to input facts you want to gather. Refer to the Fact Caching section for more information about facts.
- Click the Groups tab to configure groups for the host.
- Click the
button to associate the host with an existing group.
Available groups appear in a separate selection window.
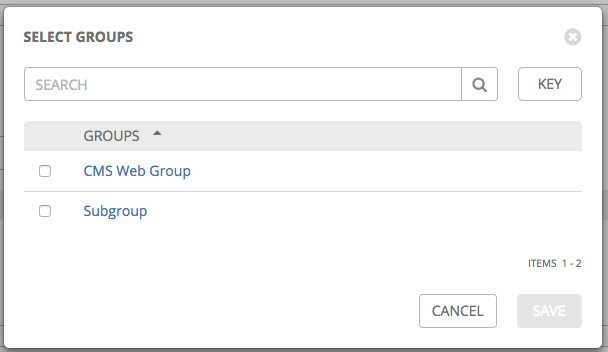
- Click to select the group(s) to associate with the host and click Save.
Once a group is associated, it displays as an entry in the list of groups associated with the host.
13.2.4. Add source¶
Inventory sources are no longer associated with groups. Prior to Ansible Tower 3.2, spawned groups and hosts would be children of our inventory source group. Now, spawned groups are top-level. These groups may still have child groups, and all of these spawned groups may have hosts.
Adding a source to an inventory only applies to standard inventories. Smart inventories inherit their source from the standard inventories they are associated with. To configure the source for the inventory:
- In the inventory you want to add a source, click the Sources tab.
- Click the
 button.
button.
This opens the Create Source window.
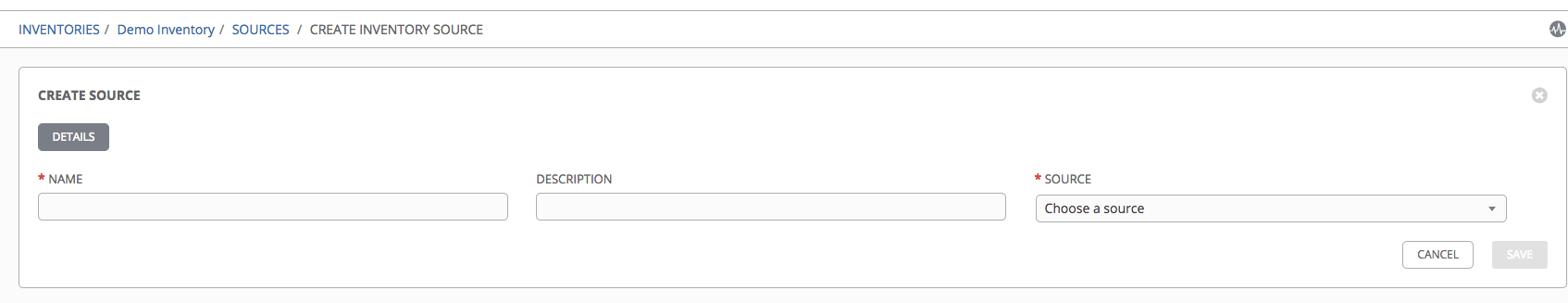
- Enter the appropriate details into the required and optional fields:
- Name: Required
- Description: Enter an arbitrary description as appropriate (optional)
- Source: Choose a source which matches the credential type against which a host can be entered. Refer to the Credential Sources section for more information about each source and details for entering the appropriate information.
Note
Starting with Ansible Tower version 3.2, support for Rackspace Cloud Servers was discontinued.
- You can configure the the level of output on any inventory source’s update jobs by selecting the appropriate option from the Verbosity drop-down menu.
- All cloud inventory sources have the following update options:
- Overwrite: Refer to the on-screen tooltip (
 ) for information. In order to guarantee consistent behavior after 3.2 migration, do not set to
) for information. In order to guarantee consistent behavior after 3.2 migration, do not set to True.
- Overwrite Variables: Refer to the on-screen tooltip (
 ) for information.
) for information. - Update on Launch: Each time a job runs using this inventory, refresh the inventory from the selected source before executing job tasks. To avoid job overflows if jobs are spawned faster than the inventory can sync, selecting this allows you to configure a Cache Timeout to cache prior inventory syncs for a certain number of seconds.
The “Update on Launch” setting refers to a dependency system for projects and inventory, and it will not specifically exclude two jobs from running at the same time. If a cache timeout is specified, then the dependencies for the second job is created and it uses the project and inventory update that the first job spawned. Both jobs then wait for that project and/or inventory update to finish before proceeding. If they are different job templates, they can then both start and run at the same time, if the system has the capacity to do so.
Note
If you intend to use Tower’s provisioning callback feature with a dynamic inventory source, “Update on Launch” should be set for the inventory group.
- Review your entries and selections and click Save when done.
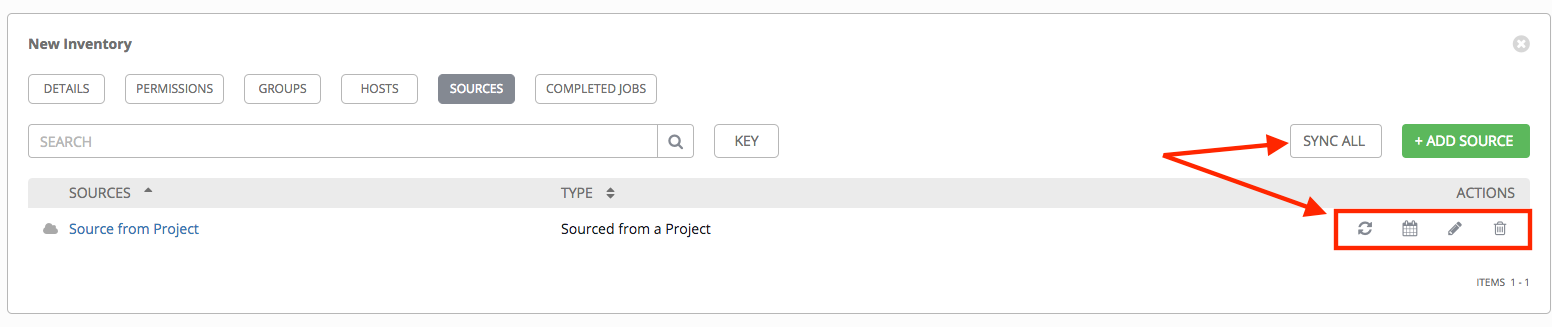
Once a source is defined, it displays as an entry in the list of sources associated with the inventory. From the Sources tab you can perform a sync on a single source, or sync all of them at once. You can also perform additional actions such as scheduling a sync process, and edit or delete the source.
- To configure notifications for the source, click the Notifications tab.
- If notifications are already set up, select a notification preference.
- if notifications have not been set up, refer to Notifications for more information.
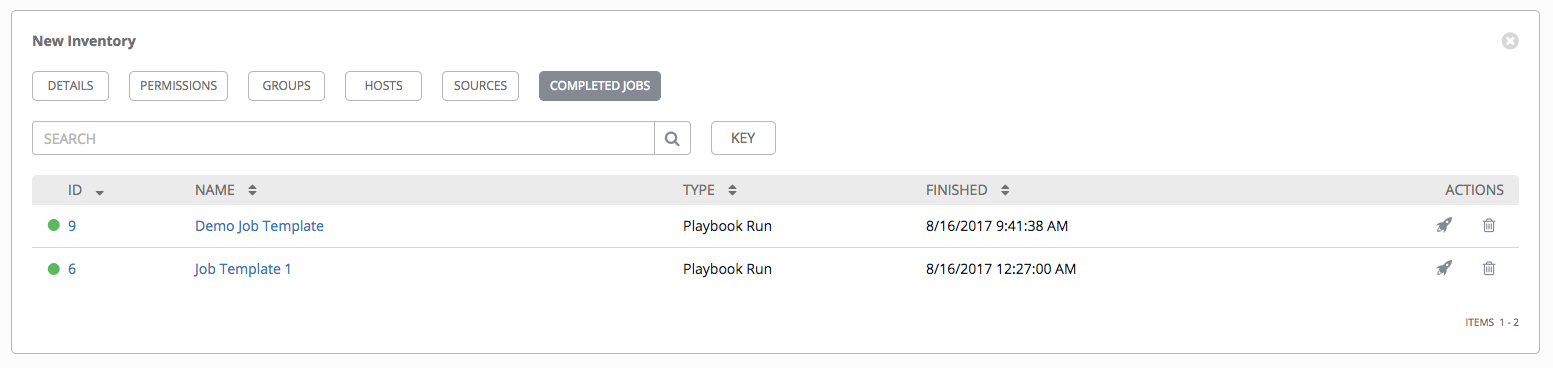
13.2.5. View completed jobs¶
If an inventory was used to run a job, you can view details about those jobs in the Completed Jobs tab of the inventory.
13.2.5.1. Smart Host Filter¶
You can use a search filter to populate hosts for an inventory. This feature was introduced in Ansible Tower 3.2 utilizing the capability of the fact searching feature.
Facts generated by an Ansible playbook during a Job Template run are stored by Tower into the database whenever use_fact_cache=True is set per-Job Template. New facts are merged with existing facts and are per-host. These stored facts can be used to filter hosts via the /api/v2/hosts endpoint, using the GET query parameter host_filter For example: /api/v2/hosts?host_filter=ansible_facts__ansible_processor_vcpus=8
The host_filter parameter allows for:
- grouping via ()
- use of the boolean and operator:
__to reference related fields in relational fields__is used on ansible_facts to separate keys in a JSON key path[]is used to denote a json array in the path specification""can be used in the value when spaces are wanted in the value
- “classic” Django queries may be embedded in the
host_filter
Examples:
/api/v2/hosts/?host_filter=name=localhost
/api/v2/hosts/?host_filter=ansible_facts__ansible_date_time__weekday_number="3"
/api/v2/hosts/?host_filter=ansible_facts__ansible_processor[]="GenuineIntel"
/api/v2/hosts/?host_filter=ansible_facts__ansible_lo__ipv6[]__scope="host"
/api/v2/hosts/?host_filter=ansible_facts__ansible_processor_vcpus=8
/api/v2/hosts/?host_filter=ansible_facts__ansible_env__PYTHONUNBUFFERED="true"
/api/v2/hosts/?host_filter=(name=localhost or name=database) and (groups__name=east or groups__name="west coast") and ansible_facts__an
13.2.5.2. Credential Sources¶
Topics:
Choose a source which matches the credential type against which a host can be entered.
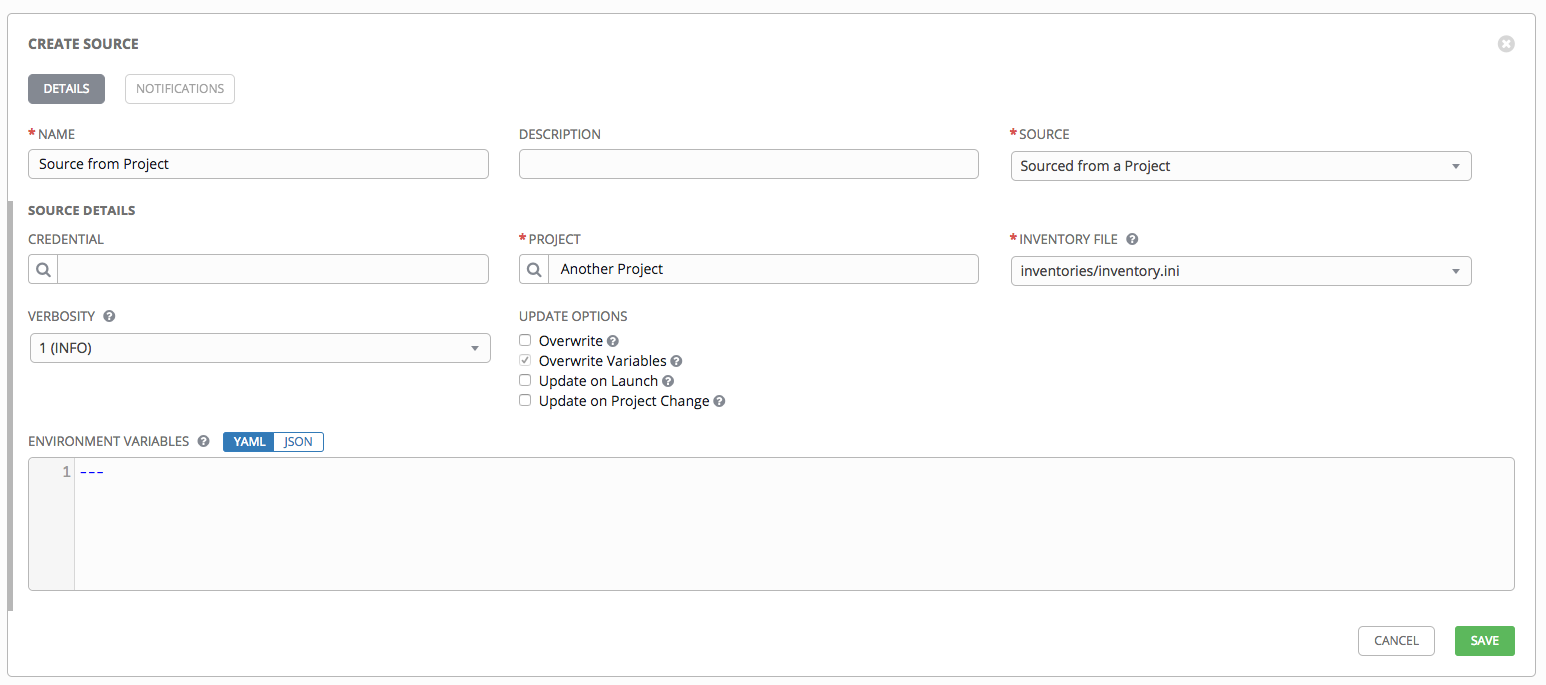
13.2.5.2.1. Sourced from a Project¶
An inventory that is sourced from a project means that is uses the SCM type from the project it is tied to. For example, if the project’s source is from GitHub, or a Red Hat Insights project, then the inventory will use the same source.
- To configure a project-sourced inventory, select Sourced from a Project from the Source field.
- The Create Source window expands with additional fields. Enter the following details:
- Credential: Specify the credential to use for this source.
- Project: Required. Specify the project this inventory is using as its source. Click the
button to choose from a list of projects. If the list is extensive, use the search to narrow the options.
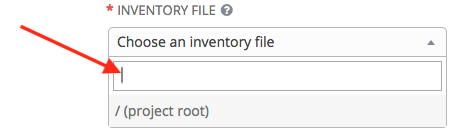
- Inventory File: Required. Select an inventory file associated with the sourced project. If not already populated, you can type it into the text field within the drop down menu to filter the extraneous file types.
- In addition to the update options available for cloud inventory sources, you can specify whether or not to update on project changes. Check the Update on Project Change option to refresh the inventory from the selected source after every project update where the SCM revision changes before executing job tasks.
- In order to pass to the custom inventory script, you can optionally set environment variables in the Environment Variables field.
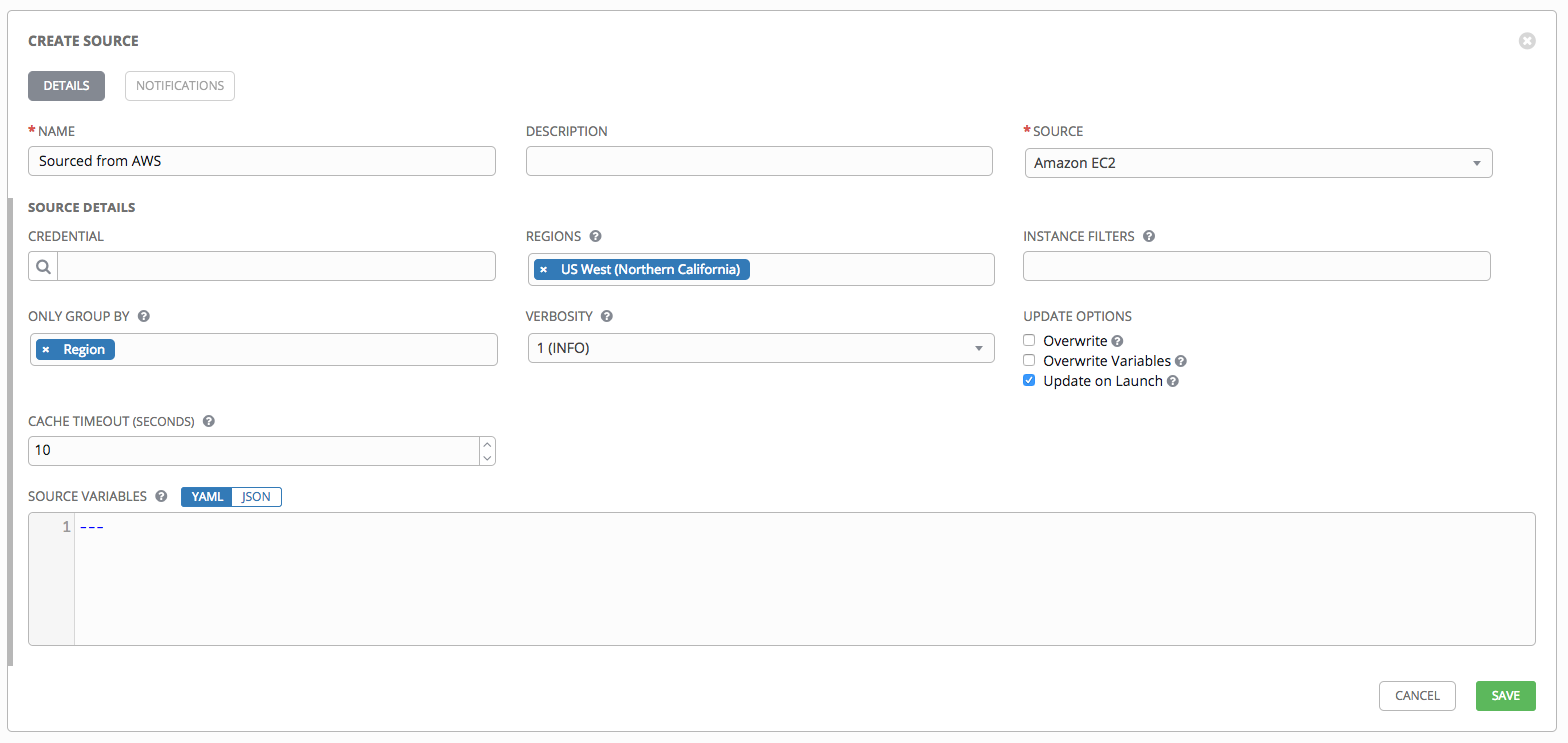
13.2.5.2.2. Amazon Web Services EC2¶
- To configure an AWS EC2-sourced inventory, select Amazon EC2 from the Source field.
- The Create Source window expands with additional fields. Enter the following details:
Credential: Choose from an existing credential (for more information, refer to Credentials).
If Tower is running on an EC2 instance with an assigned IAM Role, the credential may be omitted, and the security credentials from the instance metadata will be used instead. For more information on using IAM Roles, refer to the IAM_Roles_for_Amazon_EC2_documentation_at_Amazon.
Regions: Click on the regions field to see a list of regions for your cloud provider. You can select multiple regions, or choose “All” to include all regions. Tower will only be updated with Hosts associated with the selected regions.
Instance Filters: Rather than importing your entire Amazon EC2 inventory, filter the instances returned by the inventory script based on a variety of metadata. Hosts are imported if they match any of the filters entered here.
Examples:
- To limit to hosts having the tag
TowerManaged: Entertag-key=TowerManaged- To limit to hosts using either the key-name
stagingorproduction: Enterkey-name=staging, key-name=production- To limit to hosts where the
Nametag begins withtest: Entertag:Name=test*For more information on the filters that can be used here, refer to the Describe Instances documentation at Amazon.
Only Group By: By default, Tower creates groups based on the following Amazon EC2 parameters:
- Availability Zones
- Image ID
- Instance ID
- Instance Type
- Key Name
- Region
- Security Group
- Tags (by name)
- VPC ID
- Tag None
If you do not want all these groups created, select from the dropdown the list of groups that you would like created by default. You can also select
Instance IDto create groups based on the Instance ID of your instances.
- Use the Source Variables field to override variables found in
ec2.iniand used by the inventory update script. Enter variables using either JSON or YAML syntax. Use the radio button to toggle between the two. For a detailed description of these variables view ec2.ini in the Ansible GitHub repo.
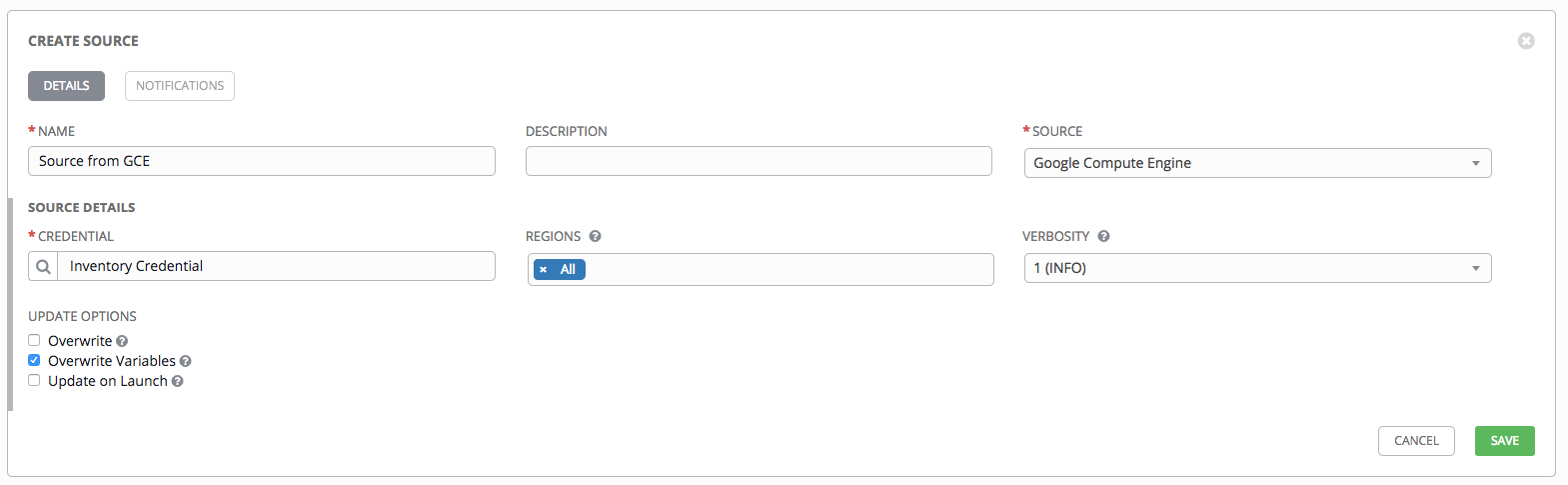
13.2.5.2.3. Google Compute Engine¶
- To configure a Google-sourced inventory, select Google Compute Engine from the Source field.
- The Create Source window expands with additional fields. Enter the following details:
- Credential: Required. Choose from an existing Credential. For more information, refer to Credentials.
Note
If you are using a GCE credential for an inventory sync, be sure that the Google project ID was specified when the credential was created.
- Regions: Click on the regions field to see a list of regions for your cloud provider. You can select multiple regions, or choose “All” to include all regions. Tower will only be updated with Hosts associated with the selected regions.
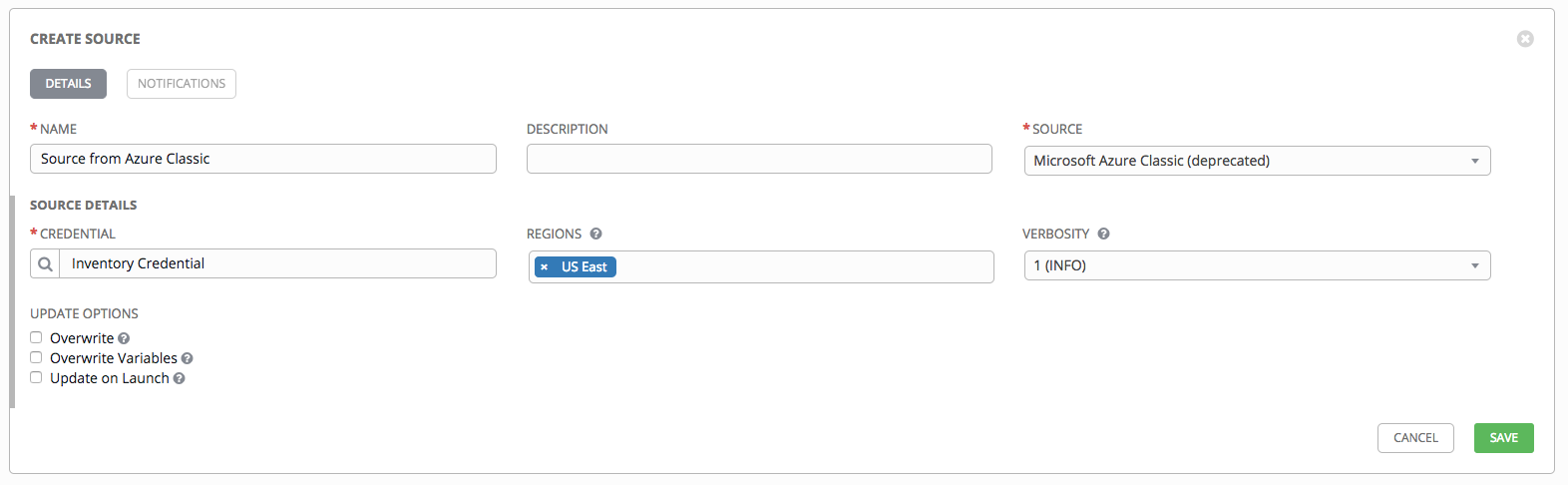
13.2.5.2.4. Microsoft Azure Classic (deprecated)¶
- To configure a Azure-sourced inventory, select Microsoft Azure Classic (deprecated) from the Source field.
- The Create Source window expands with additional fields. Enter the following details:
- Credential: Required. Choose from an existing Credential. For more information, refer to Credentials.
- Regions: Click on the regions field to see a list of regions for your cloud provider. You can select multiple regions, or choose “All” to include all regions. Tower will only be updated with Hosts associated with the selected regions.
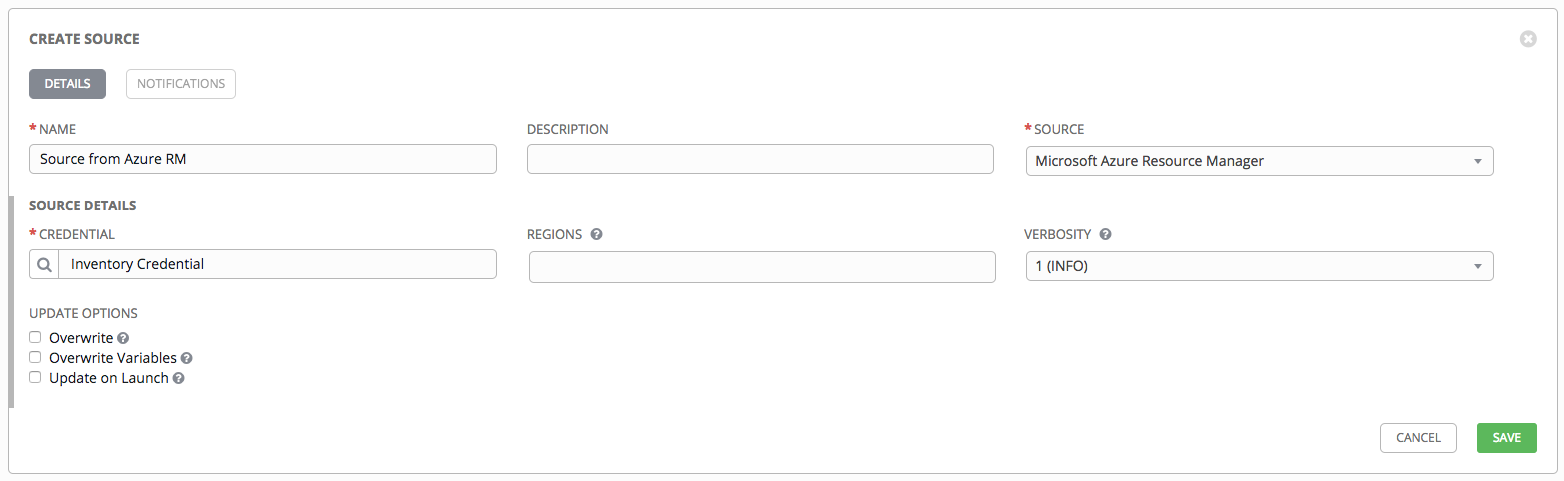
13.2.5.2.5. Microsoft Azure Resource Manager¶
- To configure a Azure Resource Manager-sourced inventory, select Microsoft Azure Resource Manager from the Source field.
- The Create Source window expands with additional fields. Enter the following details:
- Credential: Required. Choose from an existing Credential. For more information, refer to Credentials.
- Regions: Click on the regions field to see a list of regions for your cloud provider. You can select multiple regions, or choose “All” to include all regions. Tower will only be updated with Hosts associated with the selected regions.
13.2.5.2.6. VMware vCenter¶
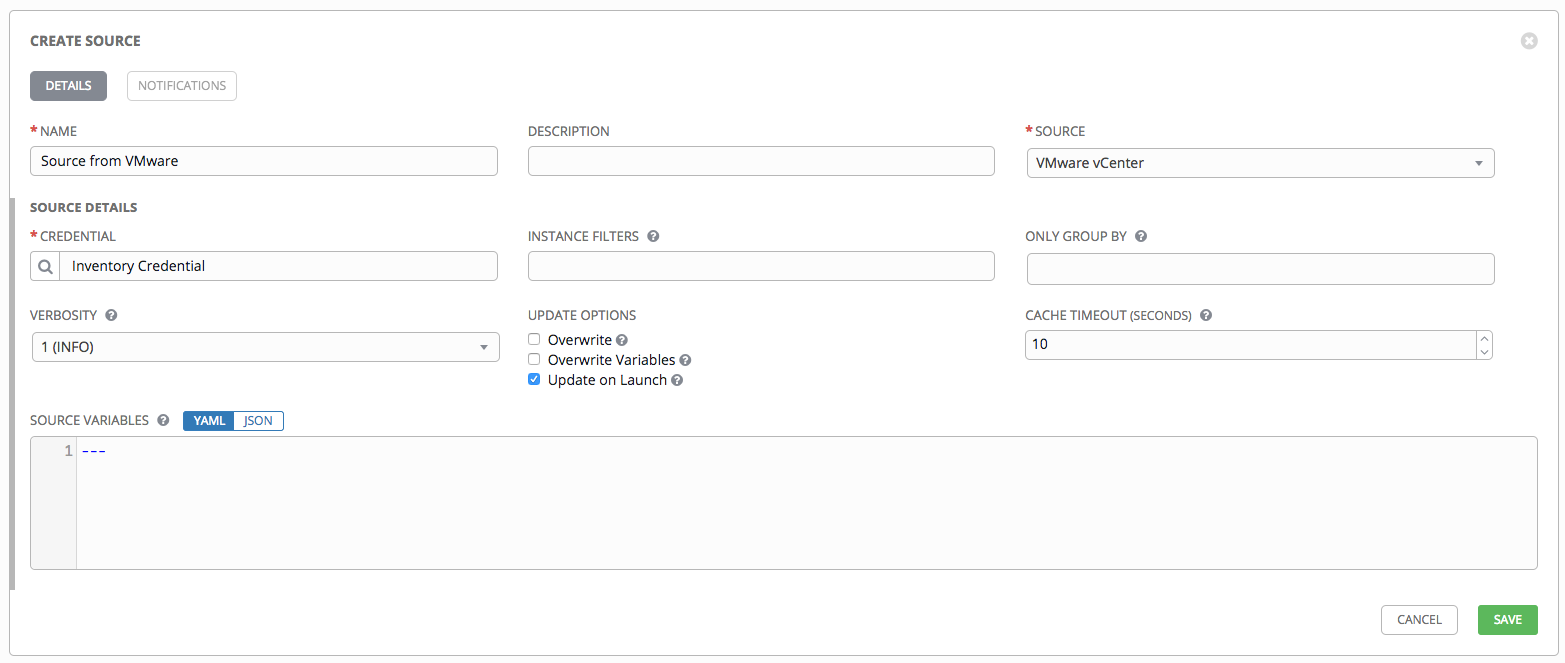
- To configure a VMWare-sourced inventory, select VMware vCenter from the Source field.
- The Create Source window expands with additional fields. Enter the following details:
- Credential: Required. Choose from an existing credential (for more information, refer to Credentials).
- Instance Filters: Rather than importing your entire VMWare inventory, filter the instances returned by the inventory script based on a variety of metadata. Hosts are imported if they match any of the filters entered here.
For more information on the filters that can be used here, refer to the Quick Filters Available for vSphere Objects documentation at VMware.
- Only Group By: By default, Tower creates groups based on user-specified VMWare parameters. For example, enter
Instance IDto create groups based on the Instance ID of your instances.
- Use the Source Variables field to override variables found in
vmware.iniand used by the inventory update script. Enter variables using either JSON or YAML syntax. Use the radio button to toggle between the two. For a detailed description of these variables view vmware_inventory.ini in the Ansible GitHub repo.
Note
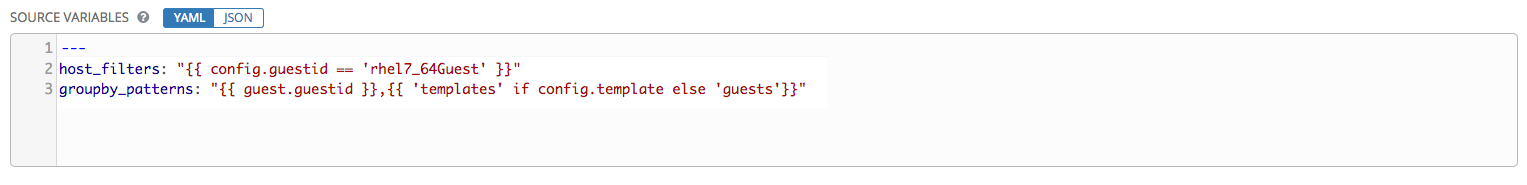
The inventory script for VMware was updated in Ansible Tower 3.1.2 to allow configuration of the host_filters or groupby_patterns parameter. Specify those values in the Source Variables text field of the Create Group screen or Edit Group screen. For example:
13.2.5.2.7. Red Hat Satellite 6¶
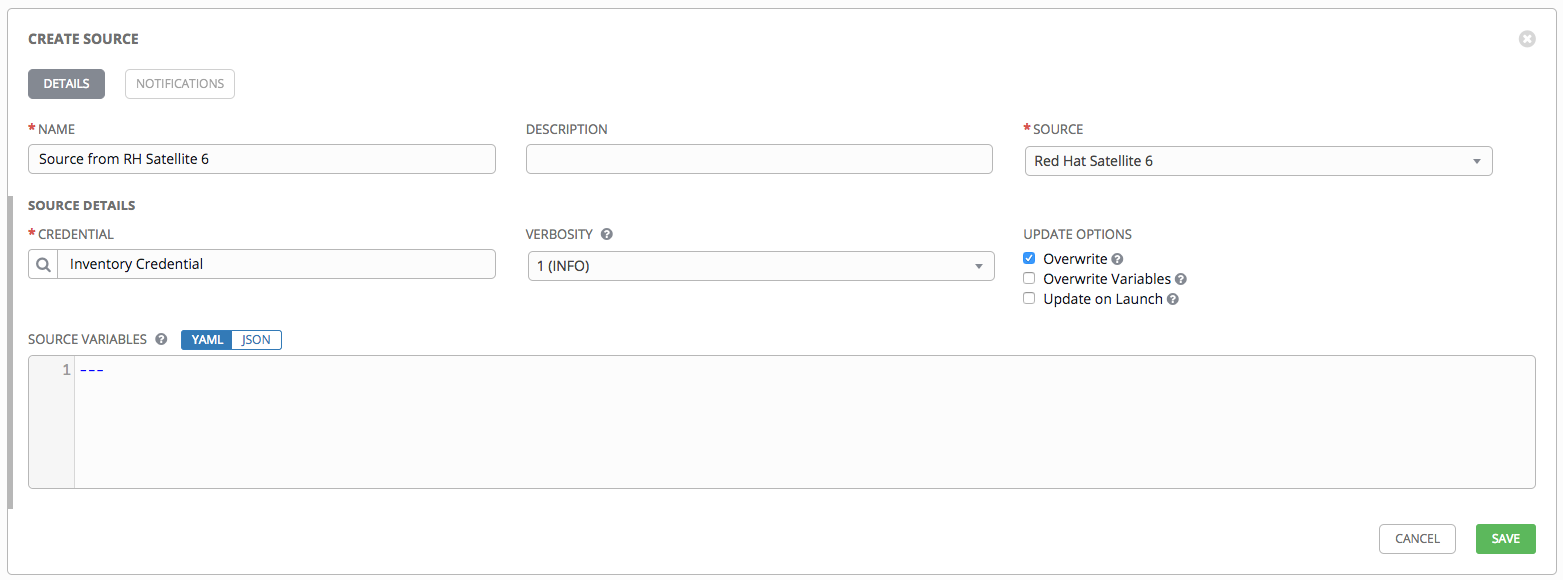
- To configure a Red Hat Satellite-sourced inventory, select Red Hat Satellite from the Source field.
- The Create Source window expands with additional fields.
- Credential: Required. Choose from an existing credential (for more information, refer to Credentials).
- Use the Source Variables field to override variables found in
foreman.iniand used by the inventory update script.
Note
The variable want_facts from foreman.ini is hard-coded to True and cannot be overridden at this time.
Enter variables using either JSON or YAML syntax. Use the radio button to toggle between the two. For a detailed description of these variables view foreman.ini in the Ansible GitHub repo.
13.2.5.2.8. Red Hat CloudForms¶
- To configure a Red Hat CloudForms-sourced inventory, select Red Hat CloudForms from the Source field.
- The Create Source window expands with additional fields. Enter the following details:
- Credential: Required. Choose from an existing credential (for more information, refer to Credentials).
- Use the Source Variables field to override variables found in
cloudforms.iniand used by the inventory update script. Enter variables using either JSON or YAML syntax. Use the radio button to toggle between the two. For a detailed description of these variables view cloudforms.ini in the Ansible GitHub repo.
13.2.5.2.9. OpenStack¶
- To configure an OpenStack-sourced inventory, select OpenStack from the Source field.
- The Create Source window expands with additional fields. Enter the following details:
- Credential: Required. Choose from an existing credential (for more information, refer to Credentials).
- Use the Source Variables field to override variables found in
openstack.ymland used by the inventory update script. Enter variables using either JSON or YAML syntax. Use the radio button to toggle between the two. For a detailed description of these variables view openstack.yml in the Ansible GitHub repo.
13.2.5.2.10. Red Hat Virtualization¶
- To configure a Red Hat Virtualization-sourced inventory, select Red Hat Virtualization from the Source field.
- The Create Source window expands with additional fields. The Credential is required. Choose from an existing credential (for more information, refer to Credentials).
13.2.5.2.11. Ansible Tower¶
- To configure a Ansible Tower-sourced inventory, select Ansible Tower from the Source field.
- The Create Source window expands with additional fields. Enter the following details:
- Credential: Required. Choose from an existing credential (for more information, refer to Credentials).
- Instance Filters: Rather than importing your entire Tower inventory, filter the instances by an inventory ID/name; then the inventory script would return that inventory from the other Tower instance.
13.2.5.2.12. Custom Script¶
Tower allows you to use a custom dynamic inventory script, if your administrator has added one.
- To configure a Custom Script-sourced inventory, select Custom Script from the Source field.
- The Create Source window expands with additional fields. Enter the following details:
- Credential: You can optionally provide a credential for custom sources. The kind of credential is limited to cloud and network. Refer to Custom Credential Types for more information.
- Custom Inventory Script: Required. Choose from an existing Inventory Script (for more information, refer to Custom Inventory Scripts).
- Environment Variables: Set variables in the environment to be used by the inventory update script. The variables would be specific to the script that you have written. Enter variables using either JSON or YAML syntax. Use the radio button to toggle between the two.
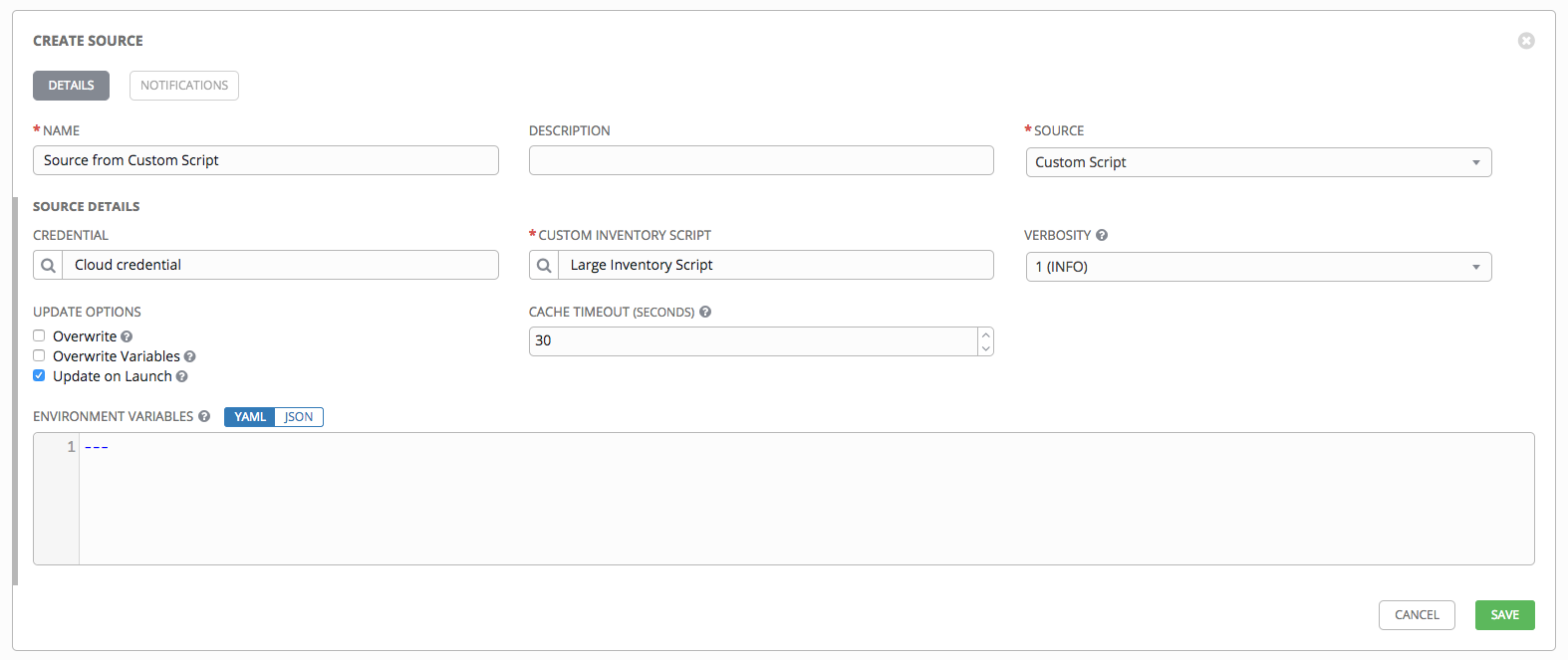
For more information on syncing or using custom inventory scripts, refer to Custom Inventory Scripts in the Ansible Tower Administration Guide.
13.3. Running Ad Hoc Commands¶
To run an ad hoc command:
- Select an inventory source from the list of hosts or groups. The inventory source can be a single group or host, a selection of multiple hosts, or a selection of multiple groups.

- Click the
 button.
button.
The Execute Command window opens.
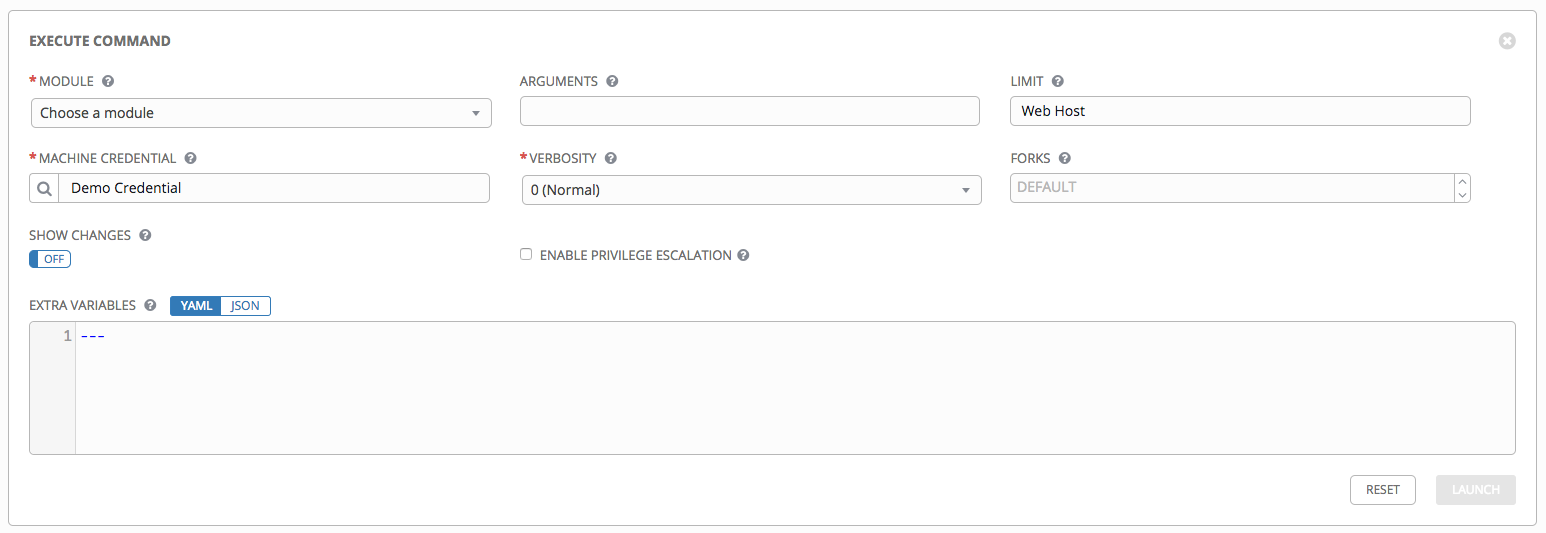
- Enter the details for the following fields:
Module: Select one of the modules that Tower supports running commands against.
command apt_repository mount win_service shell apt_rpm ping win_updates yum service selinux win_group apt group setup win_user apt_key user win_ping Arguments: Provide arguments to be used with the module you selected.
Limit: Enter the limit used to target hosts in the inventory. To target all hosts in the inventory enter
allor*, or leave the field blank. This is automatically populated with whatever was selected in the previous view prior to clicking the launch button.Machine Credential: Select the credential to use when accessing the remote hosts to run the command. Choose the credential containing the username and SSH key or password that Ansbile needs to log into the remote hosts.
Verbosity: Select a verbosity level for the standard output.
Forks: If needed, select the number of parallel or simultaneous processes to use while executing the command.
Show Changes: Select to enable the display of Ansible changes in the standard output. The default is OFF.
Enable Privilege Escalation: If enabled, the playbook is run with administrator privileges. This is the equivalent of passing the
--becomeoption to theansiblecommand.Extra Variables: Provide extra command line variables to be applied when running this inventory. Enter variables using either JSON or YAML syntax. Use the radio button to toggle between the two.
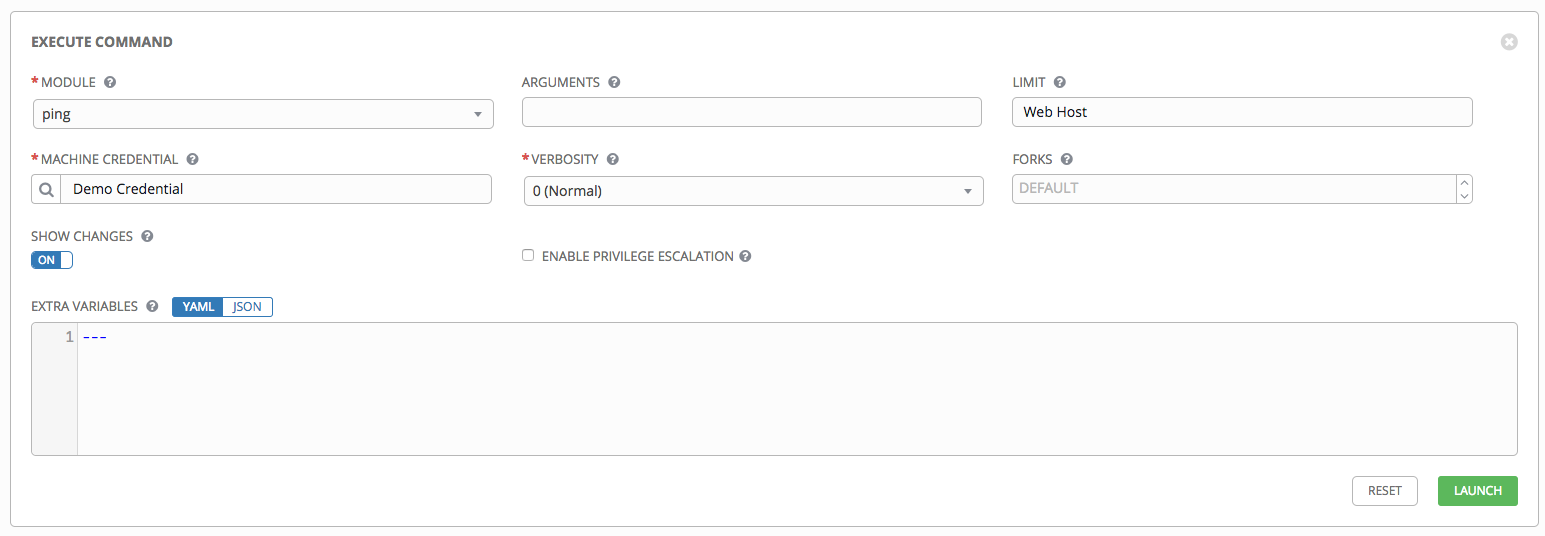
- Click the
 button to run this ad hoc command.
button to run this ad hoc command.
The results display in the Job Results and Standard Out window.