Known Issues¶
Launching the ansible-runner component not working as expected
Deleted default orgs produces duplicate Ansible-Galaxy credentials
Default LDAP directory must be configured to use LDAP Authentication
Potential security issue using
X_FORWARDED_FORinREMOTE_HOST_HEADERSReactivating OAuth authentication accounts which have been deleted
The CSRF_TRUSTED_ORIGIN setting¶
The CSRF_TRUSTED_ORIGIN setting may be required if you are using controller behind a load balancer. With the update to Django 4.2, CSRF (Cross Sight Request Forgery) checking is more strict. Because of this, using controller behind a load balancer can cause issues when it previously worked. If you encounter an error like the following, you will need to add the sources to the CSRF_TRUSTED_ORIGIN settings.
WARNING [b336a554] django.security.csrf Forbidden (Origin checking failed - https://localhost:3001 does not match any trusted origins.): /api/login/
Refer to the Django csrf-trusted-origins documentation for further detail on how to resolve this error.
Launching the ansible-runner component not working as expected¶
A change was made to the way the ansible-runner component is launched (the executable inside of the execution environment that the controller launches to run a playbook), introduced a backward incompatibility. It is highly recommended to always rebuild on top of the base execution environments that corresponds to the platform version you are using. This should be the ideal way to upgrade in general.
Deleted default orgs produces duplicate Ansible-Galaxy credentials¶
Despite being able to run subsequent installs when deleting the default organization, it does not automatically remove or fix duplicate Ansible-Galaxy credentials. Refer to the KCS article on How to remove duplicated Ansible-Galaxy credentials from the database for further detail.
Isolated nodes unsupported in an OpenShift deployment¶
Isolated nodes are not currently supported when deploying automation controller in OpenShift.
Browsers ignoring the autocomplete=off setting¶
automation controller leverages the autocomplete=off attribute on forms to relay to the browser that it should not autocomplete the fields within that form. In some scenarios, however, the browser may ignore this setting and attempt to save and/or autocomplete fields. This tends to happen on forms that appear to contain login fields like username and password, such as the User form and some Settings forms. Further investigation is underway to deliver options that prevent this behavior.
Login via HTTP requires workaround¶
To access controller nodes behind your load balancer (in traditional cluster controller installs) via HTTP, refer to the procedure described in the Troubleshooting section of the Automation Controller Administration Guide.
Job slicing and limit interactions¶
When passing a limit to a Sliced Job, if the limit causes slices to have no hosts assigned, those slices will fail, causing the overall job to fail.
Misuse of job slicing can cause errors in job scheduling¶
Job slicing is intended to scale job executions horizontally. Enabling job slicing on a job template divides an inventory to be acted upon in the number of slices configured at launch time and then starts a job for each slice.
It is expected that the number of slices will be equal to or less than the number of controller nodes. Setting an extremely high number of job slices (e.g., thousands), while allowed, can cause performance degradation as the job scheduler is not designed to schedule simultaneously thousands of workflow nodes, which are what the sliced jobs become.
Default LDAP directory must be configured to use LDAP Authentication¶
The ability to configure up to six LDAP directories for authentication requires a value. On the settings page for LDAP, there is a “Default” LDAP configuration followed by five-numbered configuration slots. If the “Default” is not populated, the controller will not try to authenticate using the other directory configurations.
Potential security issue using X_FORWARDED_FOR in REMOTE_HOST_HEADERS¶
If placing controller nodes behind some sort of proxy, this may pose a security issue. This approach assumes traffic is always flowing exclusively through your load balancer, and that traffic that circumvents the load balancer is suspect to X-Forwarded-For header spoofing.
Server error when accessing SAML metadata via hostname¶
When the controller is accessed via hostname only (e.g. https://my-little-controller), trying to read the SAML metadata from /sso/metadata/saml/ generates a sp_acs_url_invalid server error.
A configuration in which uses SAML when accessing the controller via hostname only instead of an FQDN, is not supported. Doing so will generate an error that is captured in the tower.log file and in the browser with full traceback information.
SAML authentication revokes admin role upon login¶
In previous versions of automation controller, the SAML adapter did not evaluate the System Auditor or System Admin roles for a user logging in. Because of this, the login process would not change a user’s system roles that were granted through the User Interface. The adapter now has a setting called SAML User Flags Attribute Mapping to grant users logging in these roles based on either SAML attributes or roles, and the adapter defaults to removing these roles if unspecified akin to the LDAP adapter. Refer to the logic table that shows the relationship between how the role, attribute, and attribute value settings are configured and whether or not a user will be granted the System Admin/Auditor roles.
Live events status indicators¶
Live events status dots are either seen as a red or orange dot at the top of the automation controller Dashboard when something goes wrong. They are not seen at all when the system is in a healthy state. If you encounter a red or orange live events status indicator, even when your system seems fine, the following suggestions may offer a solution:
Try manually refreshing/reloading your browser page.
Try changing web browsers, as Firefox and Safari have been reported to have issues trusting self-signed certificates.
Try creating a self-signed certificate that matches your DNS and import it into your trust manually.
Try using an incognito or private browsing session.
Try disabling your browser plugins to ensure none are blocking the service.
Live event status dots are used for troubleshooting problems with your controller instance. You can collect troubleshooting help by running a sosreport. As root, run the command sosreport from your system to automatically generate a diagnostic tar file, then contact Ansible’s Support team with the collected information for further assistance. For more information on sosreport, refer to sosreport in the Automation Controller Administration Guide.
VMWare Self-Signed Certs¶
If you have a VMware instance that uses a self-signed certificate, then you will need to add the following to the Source Vars configuration of the Cloud Group:
"source_vars": ---validate_certs: False
You can set this in inventory source for VMware vCenter as follows:
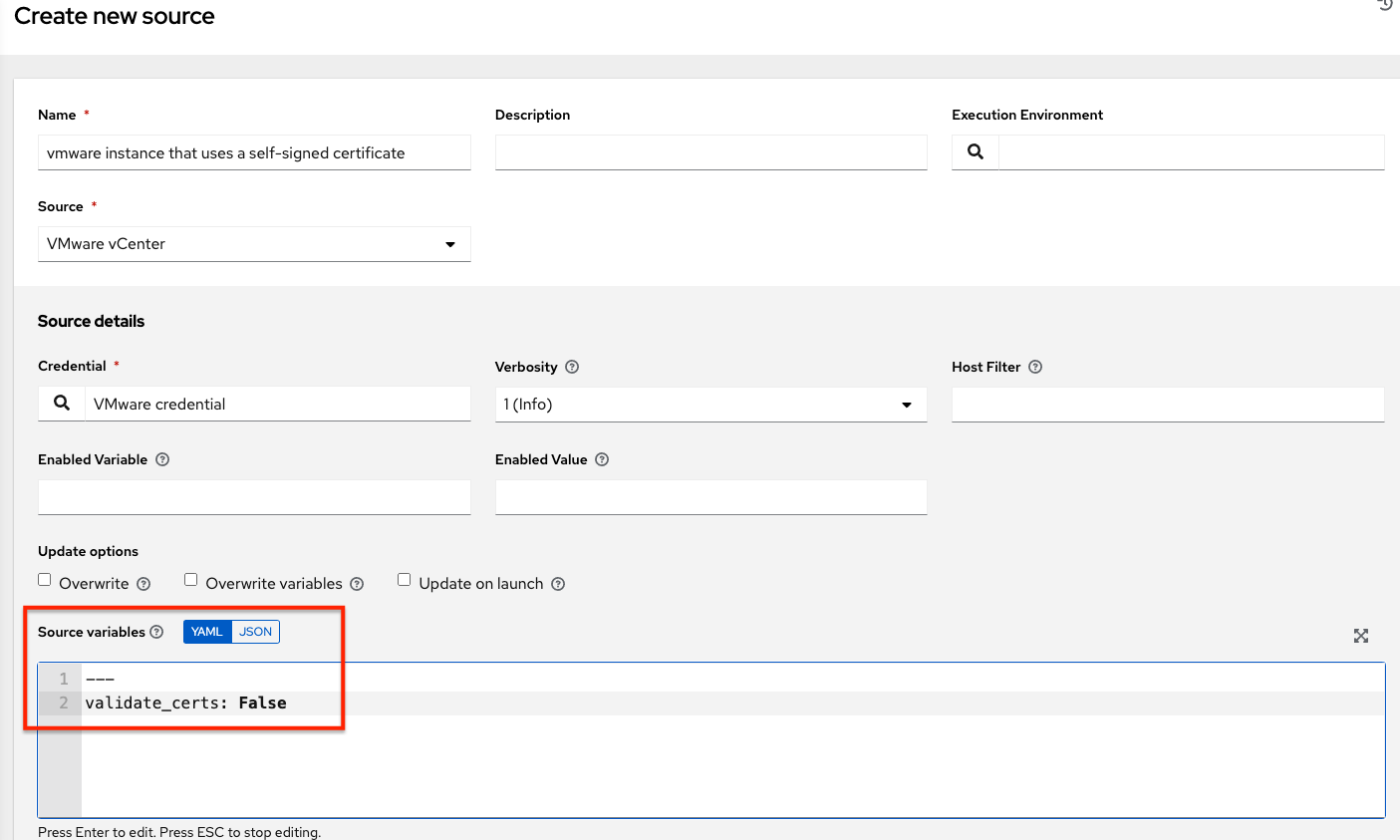
awx-manage inventory_import user¶
In general, the use of awx-manage commands is supported when executed by the root or awx user. However, in automation controller 4.0, even when run as the root user, the command awx-manage inventory_import fails to authenticate with the private registry where the Red Hat execution environments are hosted. The workaround is to run the command as the awx user, given that the images should be pre-pulled by the installer which correctly authenticates.
Database on Disk Becomes Corrupted¶
If the controller is not cleanly shutdown, it leaves a /var/lib/awx/beat.db file on disk. If that happens, the dispatcher won’t start, and you must manually delete the /var/lib/awx/beat.db file and restart the controller before the dispatcher will start properly.
Safari unable to establish connection to web socket¶
The following connection error displays in the controller:
This error is the result of Safari silently refusing to establish a connection to a web socket that is using a self-signed certificate. To resolve this issue, you must set Safari to always trust the website upon first visiting it:
Close the current browser and revisit the site. An error message appears stating Safari can’t verify the identity of the website.
Click Show Certificate.
Check the Always trust … when connecting to … checkbox to allow Safari to accept the connection.
If you click Continue without checking the checkbox, this error will persist.
Local management not functioning as expected¶
All playbooks are executed by automation controller in a Linux container called an automation execution environment.
The use of delegate_to: localhost or local_action to manage the executing host will not function in this environment, as it will still be executing inside the container.
To manage the local host where execution is running, you will need to use the ssh connection plugin to connect from the container to the local host.
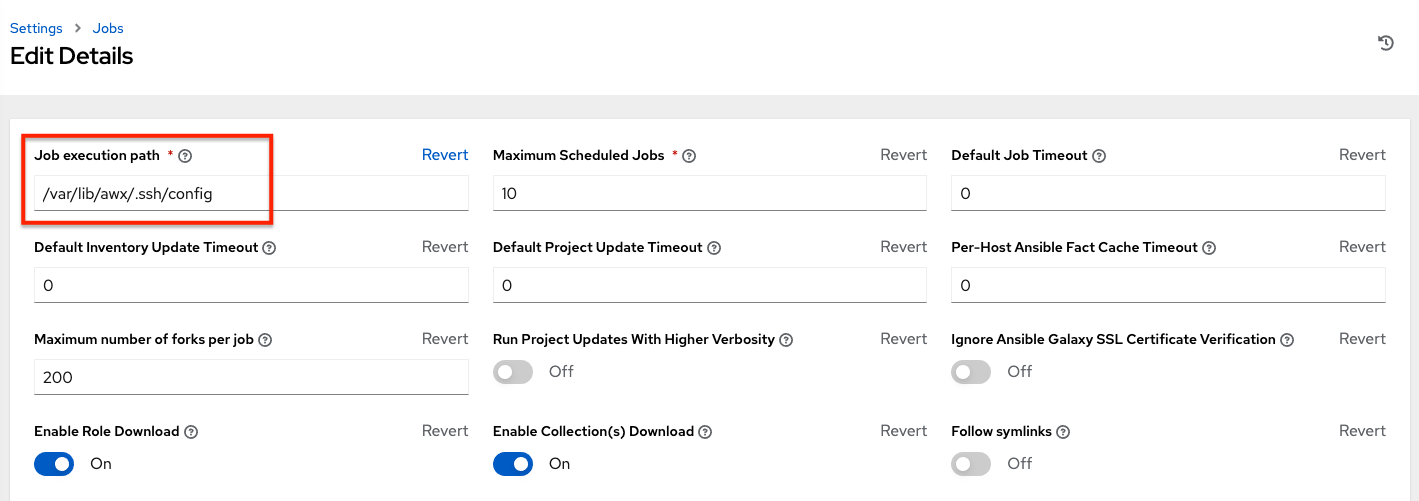
Problems when using SSH customization¶
The Job Isolation functionality in automation controller limits the directories available for playbooks to the project that is in use. If you are attempting to customize SSH behavior by using a custom SSH configuration in the awx user’s home directory, this directory must be added to the list of directories exposed to the container.
For example, to add a custom SSH config in /var/lib/awx/.ssh/config and make it available for controller jobs, you can specify the path in the Job Execution Isolation Path field accessed from the Jobs tab of the Settings screen:
Database server installed on nodes¶
All nodes in the cluster get a database server even if the nodes do not have a database. This is unexpected and may take up space.
Reactivating OAuth authentication accounts which have been deleted¶
Once a user who logs in using social authentication has been deleted, the user will not be able to login again or be recreated until the system administrator runs a cleanup_deleted action with days=0 to allow users to login again. Once cleanup_deleted has been run, the controller must be restarted using the automation-controller-service restart command. Accounts which have been deleted prior to having the cleanup_deleted action run will receive a “Your account is inactive” message upon trying to login.
Using vaulted variables in inventory sourced from a project¶
When using inventory from a source control project, individual vaulted variable values are supported. Vaulted files are not currently supported.
Saved scheduled and workflow configurations and surveys¶
If a configuration of a job template is scheduled or added to a workflow with answers from a prompted survey, changing the Job Template survey to supply different variable names may cause the saved configuration to not function. The workaround is to delete the saved schedule configuration/workflow node, and recreate it with answers from the updated survey.
