7. Credentials¶
Credentials are utilized by Tower for authentication when launching jobs against machines, synchronizing with inventory sources, and importing project content from a version control system.
Note
Tower encrypts passwords and key information in the Tower database and never makes secret information visible via the API.
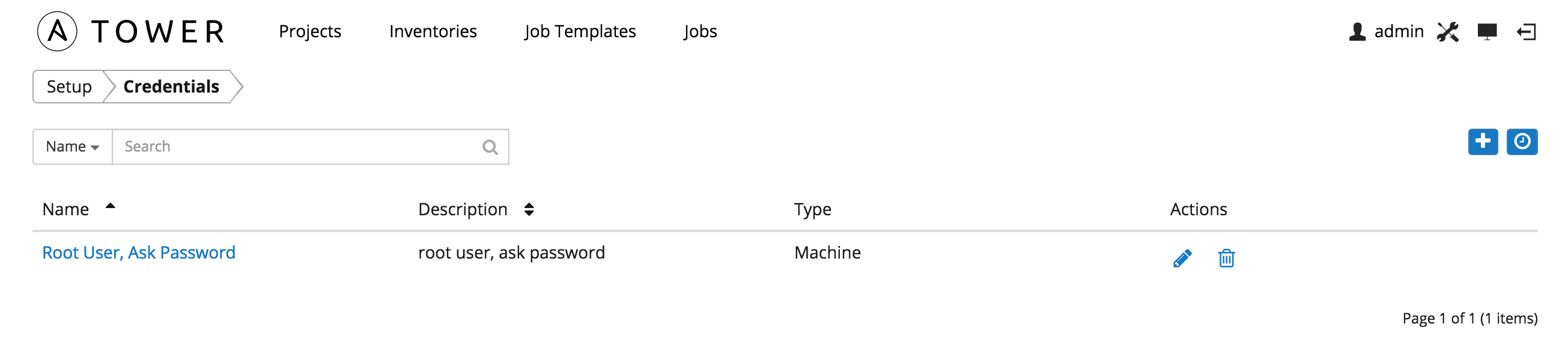
The Credentials link, accessible from the  button displays a list of all available credentials. It can be sorted and searched by Name, Description, or Type.
button displays a list of all available credentials. It can be sorted and searched by Name, Description, or Type.
Credentials can also be managed from either the Teams link or the Users link from the Setup ( ) menu. To manage credentials for teams, browse to the Teams tab and edit the appropriate team. To manage credentials for a user, browse to the Users tab and edit the appropriate user.
) menu. To manage credentials for teams, browse to the Teams tab and edit the appropriate team. To manage credentials for a user, browse to the Users tab and edit the appropriate user.
Credentials added to a Team are made available to all members of the team, whereas credentials added to a user are only available to that specific user by default.
Buttons located in the upper right corner of the Credentials screen provide the following actions:
- Create a new credential
- View Activity Stream
7.1. Add a new credential¶
Create a new credential by selecting the  button.
button.
Enter the appropriate details depending on the type of credential and select Save.
7.2. Credential Types¶
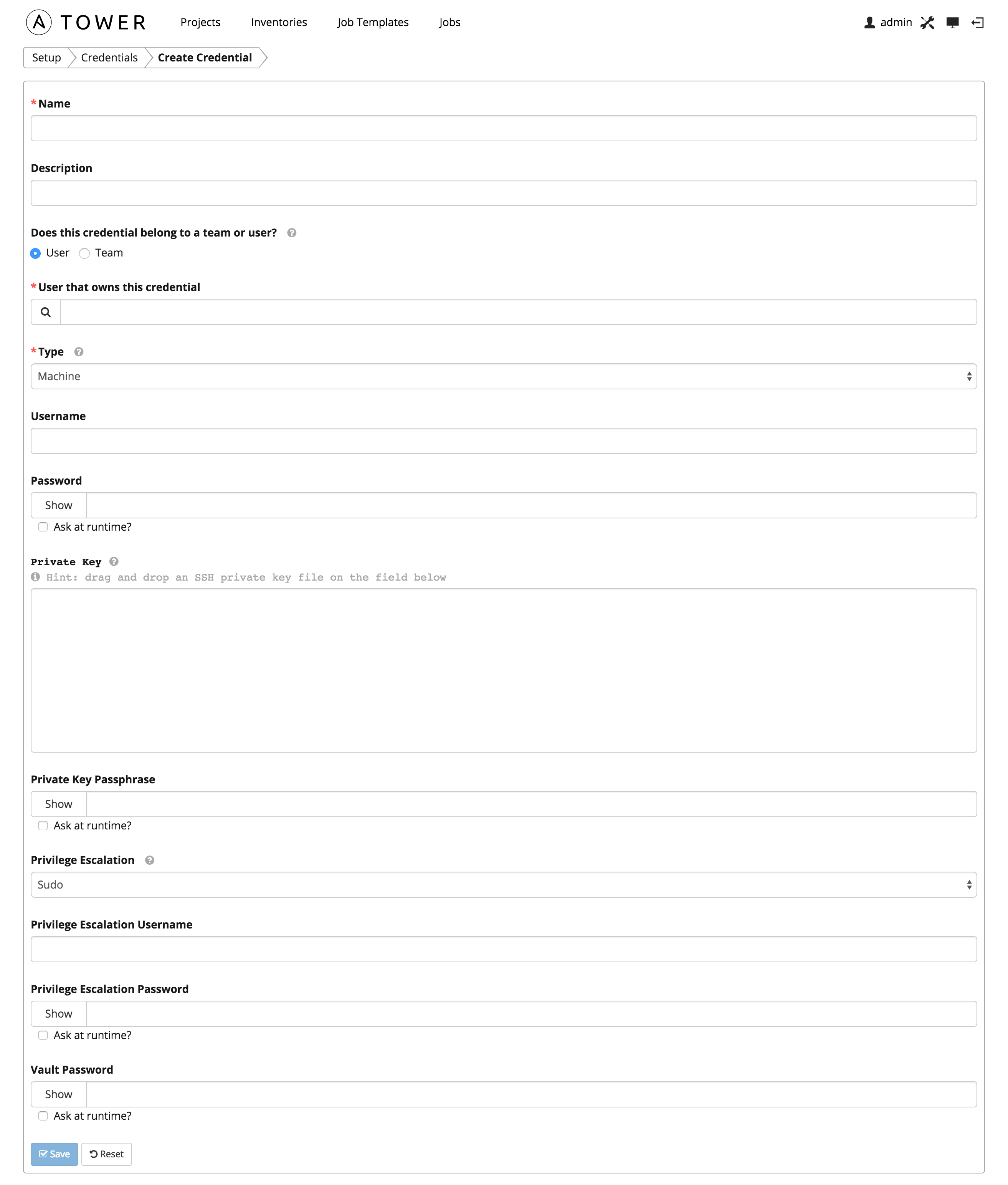
7.2.1. Machine¶
Machine credentials define ssh and user-level privilege escalation access for playbooks. They are used when submitting jobs to run playbooks on a remote host.
Machine credentials have several attributes that may be configured:
Username: The username to be used for SSH authenticatation.
Password: The actual password to be used for SSH authenticatation. This password can be stored encrypted in the Tower database, if entered. Alternatively, you can configure Tower to ask the user for the password when necessary by selecting “Ask at runtime?”. In these cases, a dialog opens when the job is launched, promoting the user to enter the password and password confirmation.
Private Key: The actual SSH Private Key to be used to authenticate the user via SSH. This key is stored encrypted in the Tower database.
Private Key Passphrase: If the SSH Private Key used is protected by a password, you can configure a Key Password for the private key. This password may be stored encrypted in the Tower database, if entered. Alternatively, you can configure Tower to ask the user for the password as necessary by selecting “Ask at runtime?”. In these cases, a dialog opens when the job is launched, prompting the user to enter the password and password confirmation.
Privilege Escalation: Specifies the type of escalation privilege to assign to specific users. This is equivalent to specifying the
--become-method=BECOME_METHODparameter, whereBECOME_METHODcould besudo | su | pbrun | pfexec.- sudo: Performs single commands with super user (root user) privileges
- su: Switches to the super user (root user) account (or to other user accounts)
- pbrun: Requests that an application or command be run in a controlled account and provides for advanced root privilege delegation and keylogging.
- pfexec: Executes commands with predefined process attributes, such as specific user or group IDs.
Privilege Escalation Username: The username to use with escalation privileges on the remote system.
Privilege Escalation Password: The actual password to be used to authenticate the user via the selected privilege escalation type on the remote system. This password may be stored encrypted in the Tower database, if entered. Alternatively, you may configure Tower to ask the user for the password when necessary by selecting “Ask at runtime?”. In these cases, a dialog opens when the job is launched, promoting the user to enter the password and password confirmation.
Note
Sudo Password must be used in combination with SSH passwords or SSH Private Keys, since Tower must first establish an authenticated SSH connection with the host prior to invoking sudo to change to the sudo user.
Vault Password: If your playbook uses Ansible Vault, add the Vault password to your credentials here. Alternatively, you may configure Tower to ask the user for the vault password when necessary by selecting “Ask at runtime?”. In these cases, a dialog opens when the job is launched, promoting the user to enter the password and password confirmation.
For more information about Ansible Vault, refer to: http://docs.ansible.com/playbooks_vault.html
Warning
Credentials which are used in Scheduled Jobs must not be configured as “Ask at runtime?”.
7.2.2. Source Control¶
Used with Projects to clone and update local source code repositories from a remote revision control system such as Git, Subversion, or Mercurial.
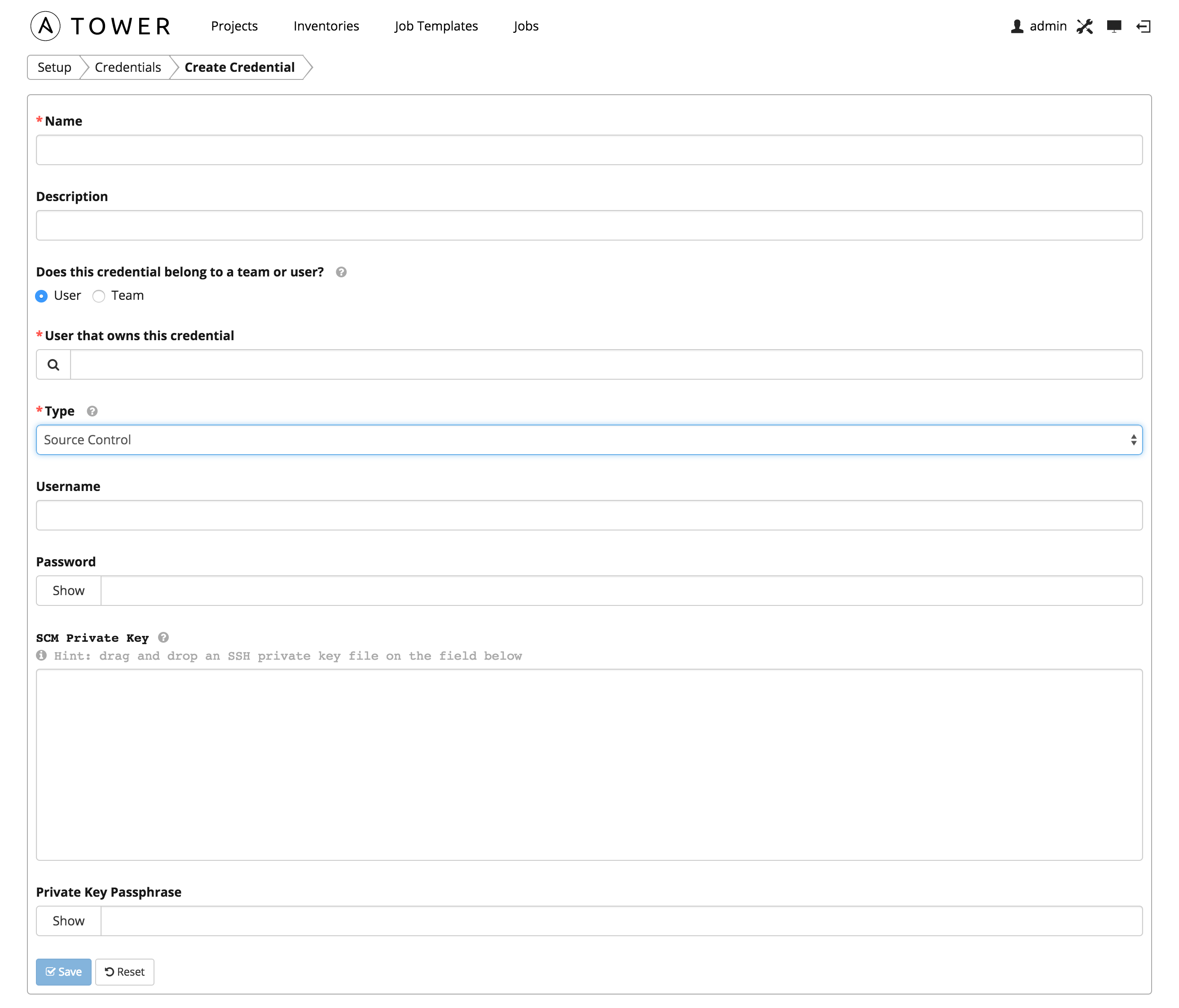
Source Control credentials have several attributes that may be configured:
- Username: The username to use in conjunction with the source control system.
- Password: The password to use in conjunction with the source control system.
- SCM Private Key: The actual SSH Private Key to be used to authenticate the user to the source control system via SSH.
- Private Key Passphrase: If the SSH Private Key used is protected by a passphrase, you may configure a Key Passphrase for the private key.
Note
Source Control credentials cannot be configured as “Ask at runtime?”.
7.2.3. Amazon Web Services¶
Enables synchronization of cloud inventory with Amazon Web Services.
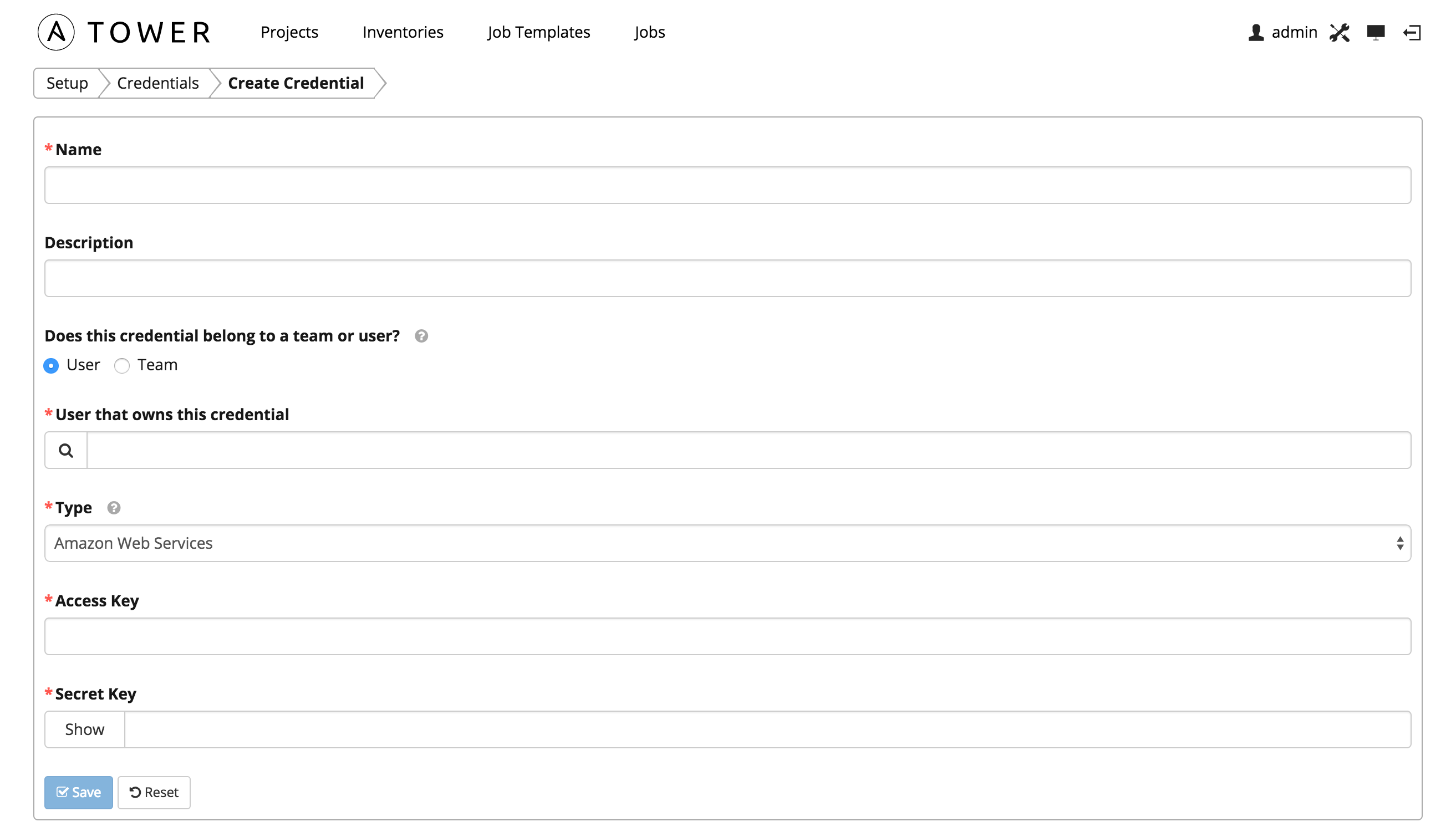
Amazon Web Services credentials consist of the AWS Access Key and Secret Key here.
7.2.4. Rackspace¶
Enables synchronization of cloud inventory with Rackspace.
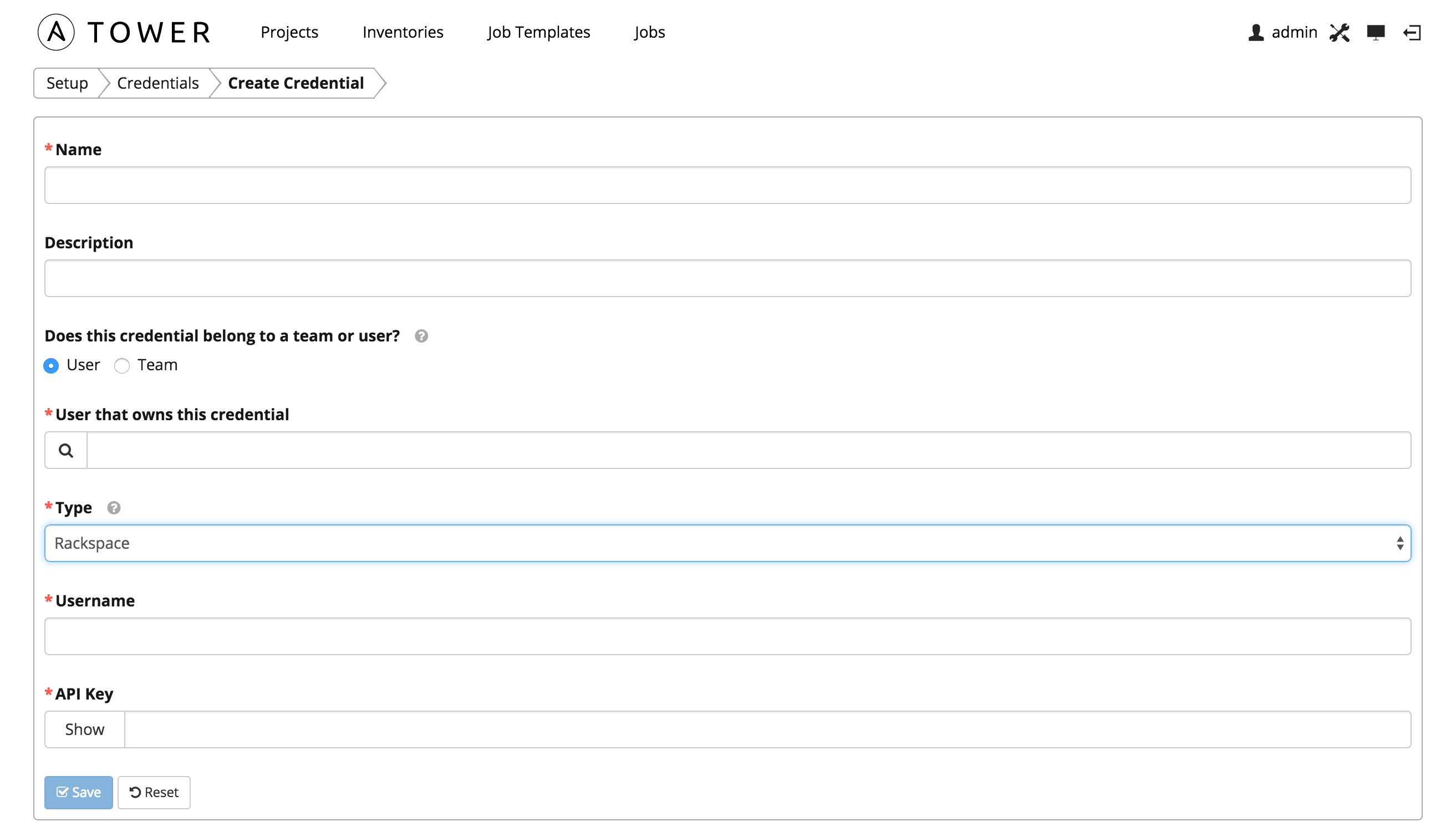
Rackspace credentials consist of the Rackspace Username and API Key.
7.2.5. VMware¶
Enables synchronization of inventory with VMware vCenter.
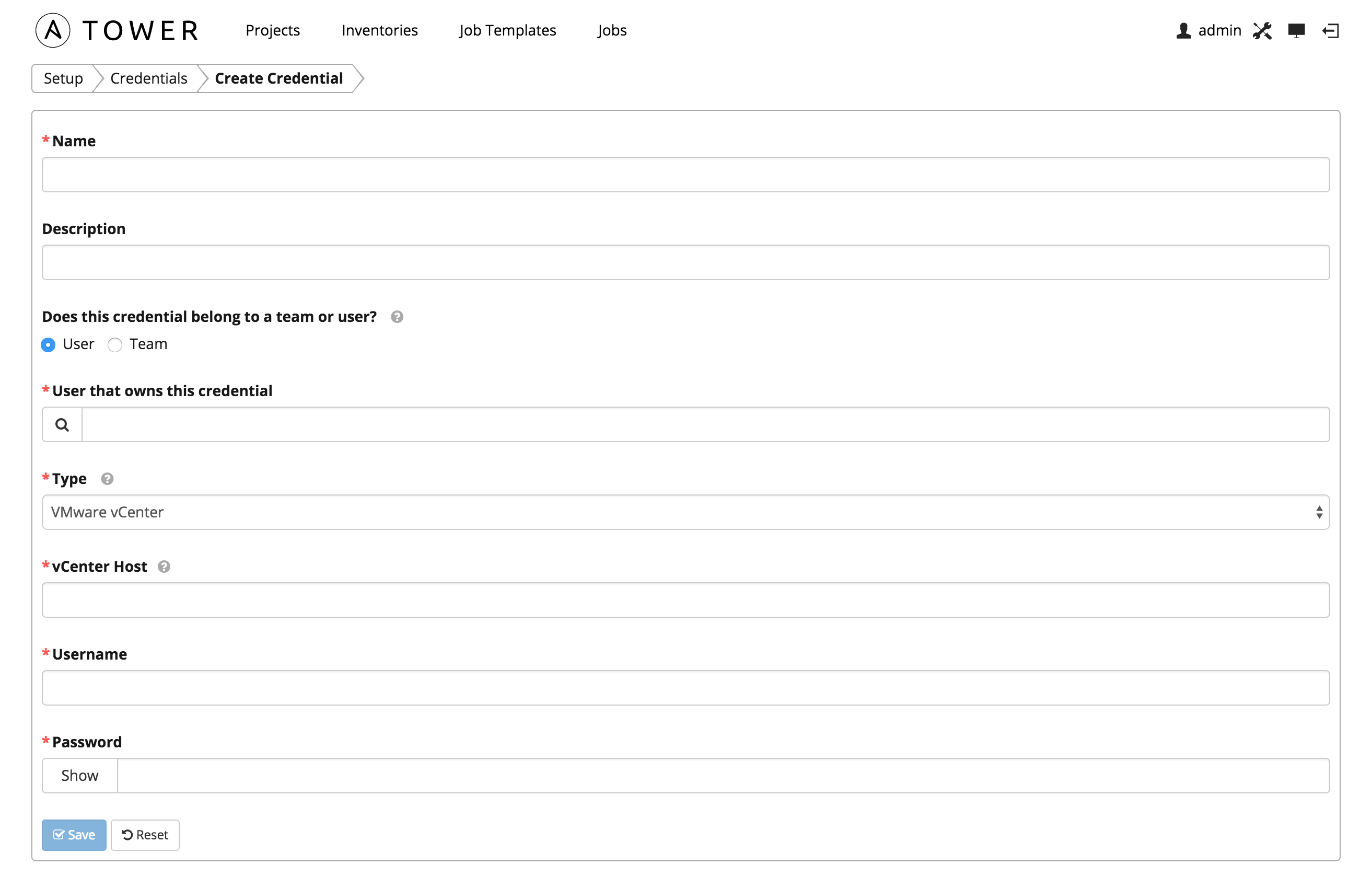
VMware credentials have several attributes that may be configured:
- vCenter Host: The vCenter hostname or IP address to connect to.
- Username: The username to use to connect to vCenter.
- Password: The password to use to connect to vCenter.
Note
If the VMware guest tools are not running on the instance, VMware inventory sync may not return an IP address for that instance.
7.2.6. Google Compute Engine¶
Enables synchronization of cloud inventory with Google Compute Engine.
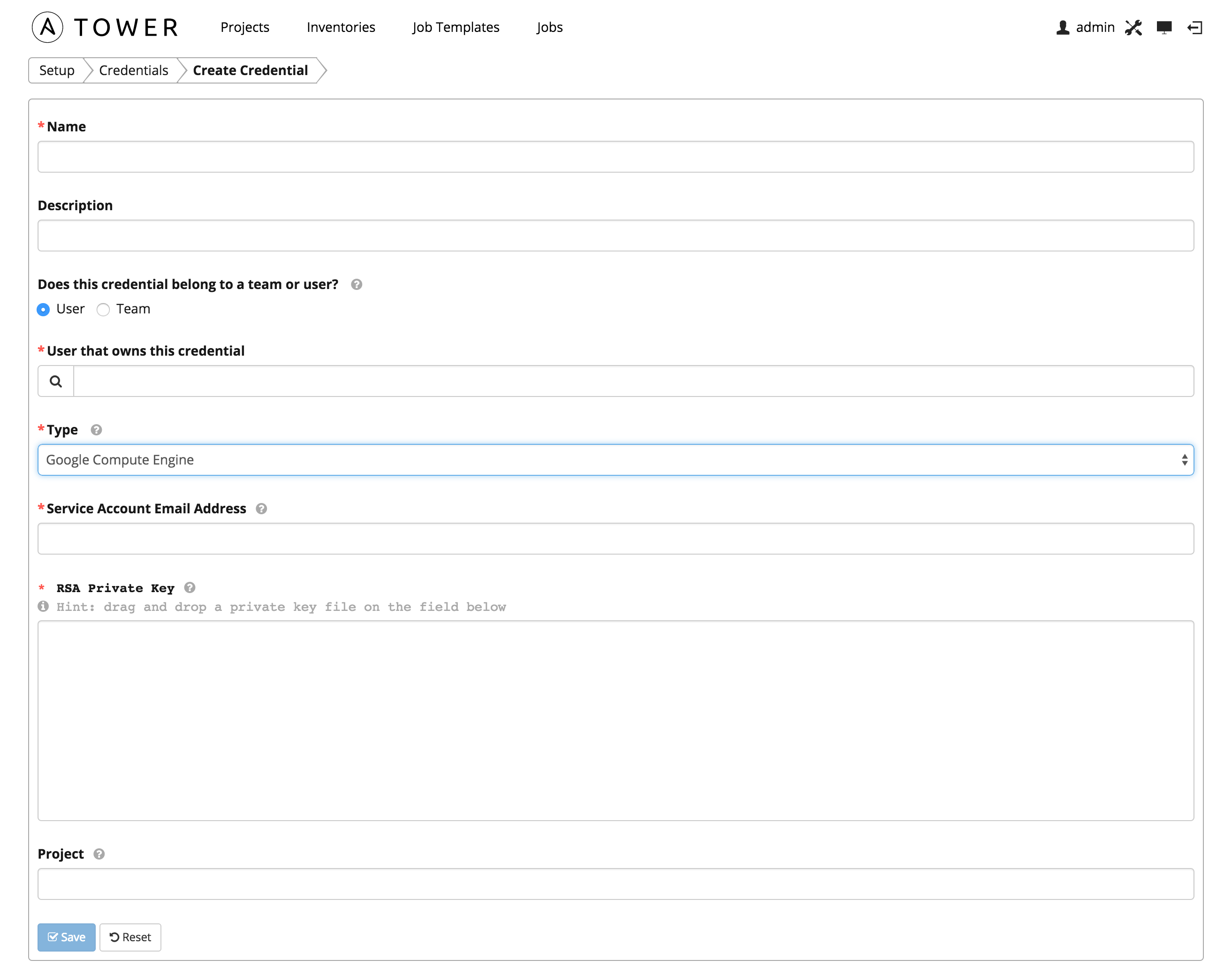
Google Compute Engine credentials have several attributes that may be configured:
- Service Account Email Address: The email address assigned to the Google Compute Engine service account.
- RSA Private Key: The PEM file associated with the service account email.
- Project: The GCE assigned identification. It is constructed as two words followed by a three digit number, such as: squeamish-ossifrage-123.
7.2.7. Microsoft Azure¶
Enables synchronization of cloud inventory with Windows Azure.
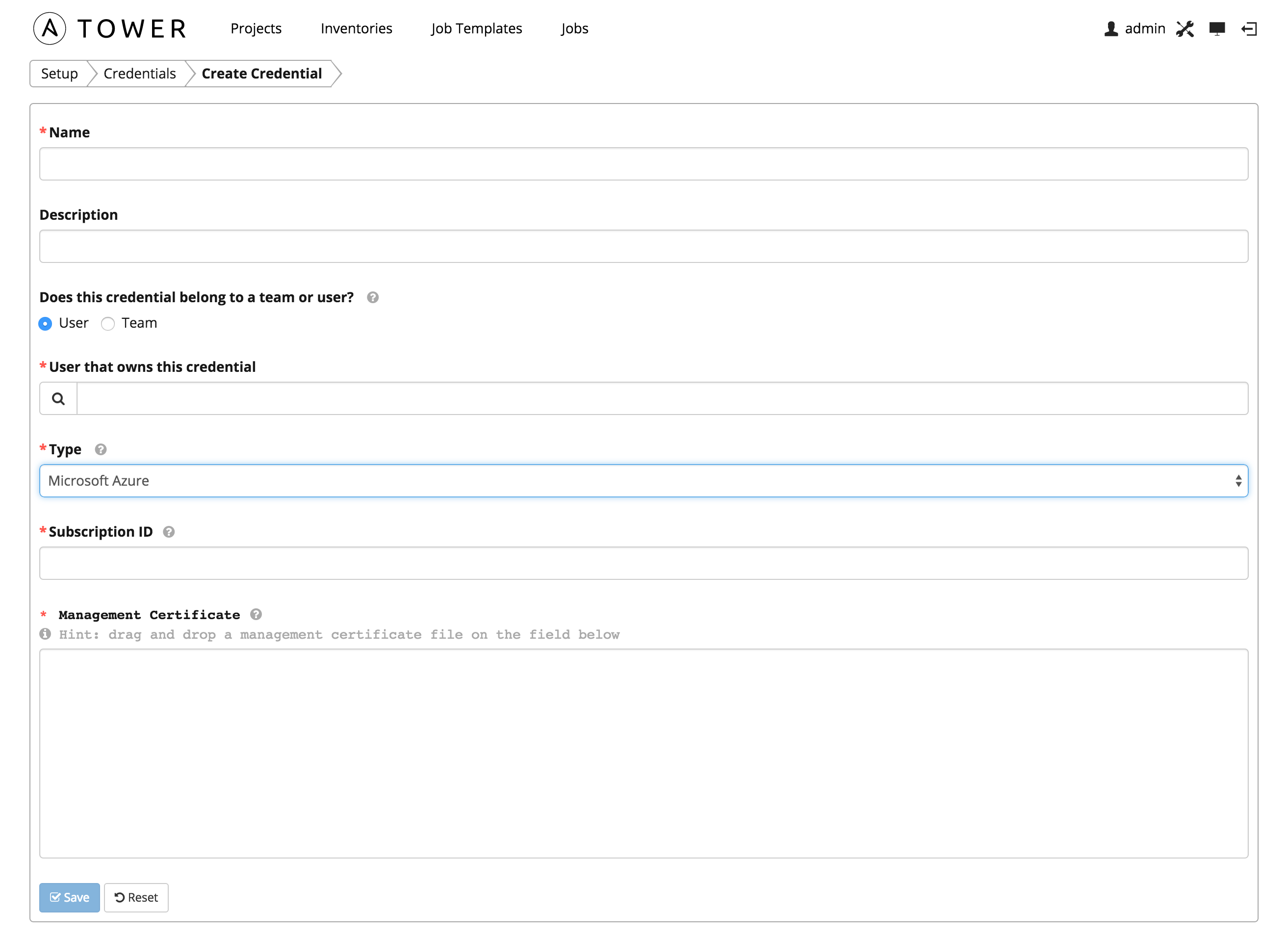
Microsoft Azure credentials have several attributes that may be configured:
- Subscription ID: The Subscription UUID for the Microsoft Azure account.
- Management Certificate: The PEM file that corresponds to the certificate you uploaded in the Microsoft Azure console.
7.2.8. OpenStack¶
Enables synchronization of cloud inventory with OpenStack.
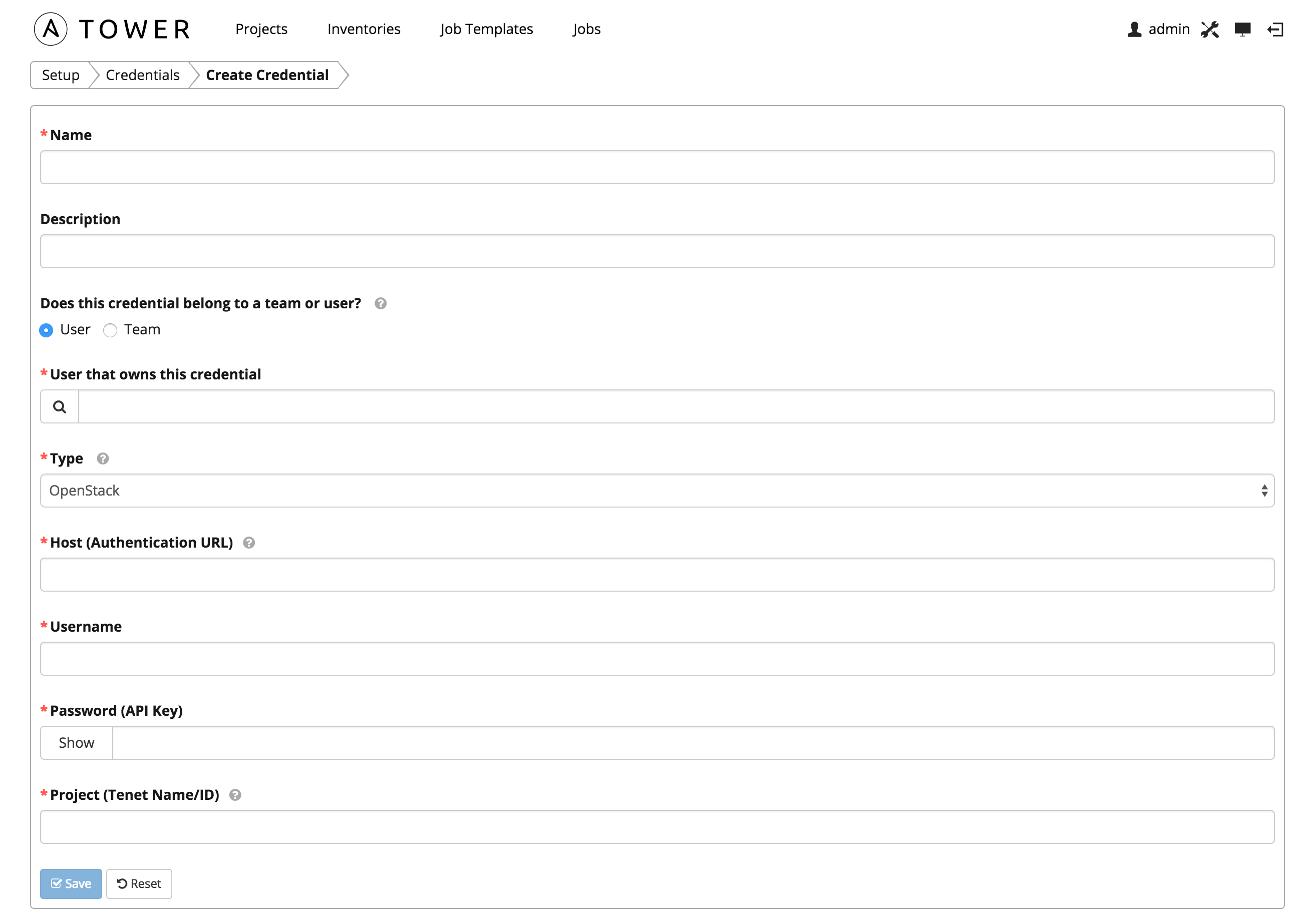
OpenStack credentials have several attributes that may be configured:
- Host (Authentication URL): The host to be used for authentication.
- Username: The username to use to connect to OpenStack.
- Password (API Key): The password or API key to use to connect to OpenStack.
- Project (Tenet Name/ID): The tenant name or tenant id used for OpenStack. This value is usually the same as the username.
