3. Custom Inventory Scripts¶
Tower includes built-in support for syncing dynamic inventory from cloud sources such as Amazon AWS, Google Compute Engine, and Rackspace, among others. Tower also offers the ability to use a custom script to pull from your own inventory source.
Note
With the release of Ansible Tower 2.4.0, edits and additions to Inventory host variables now persist beyond an inventory sync as long as --overwrite_vars is not set. To have inventory syncs behave as they did before, it is now required that both --overwrite and --overwrite_vars are set.
To manage the custom inventory scripts available in Tower, choose Inventory Scripts from the Setup ( ) menu.
) menu.
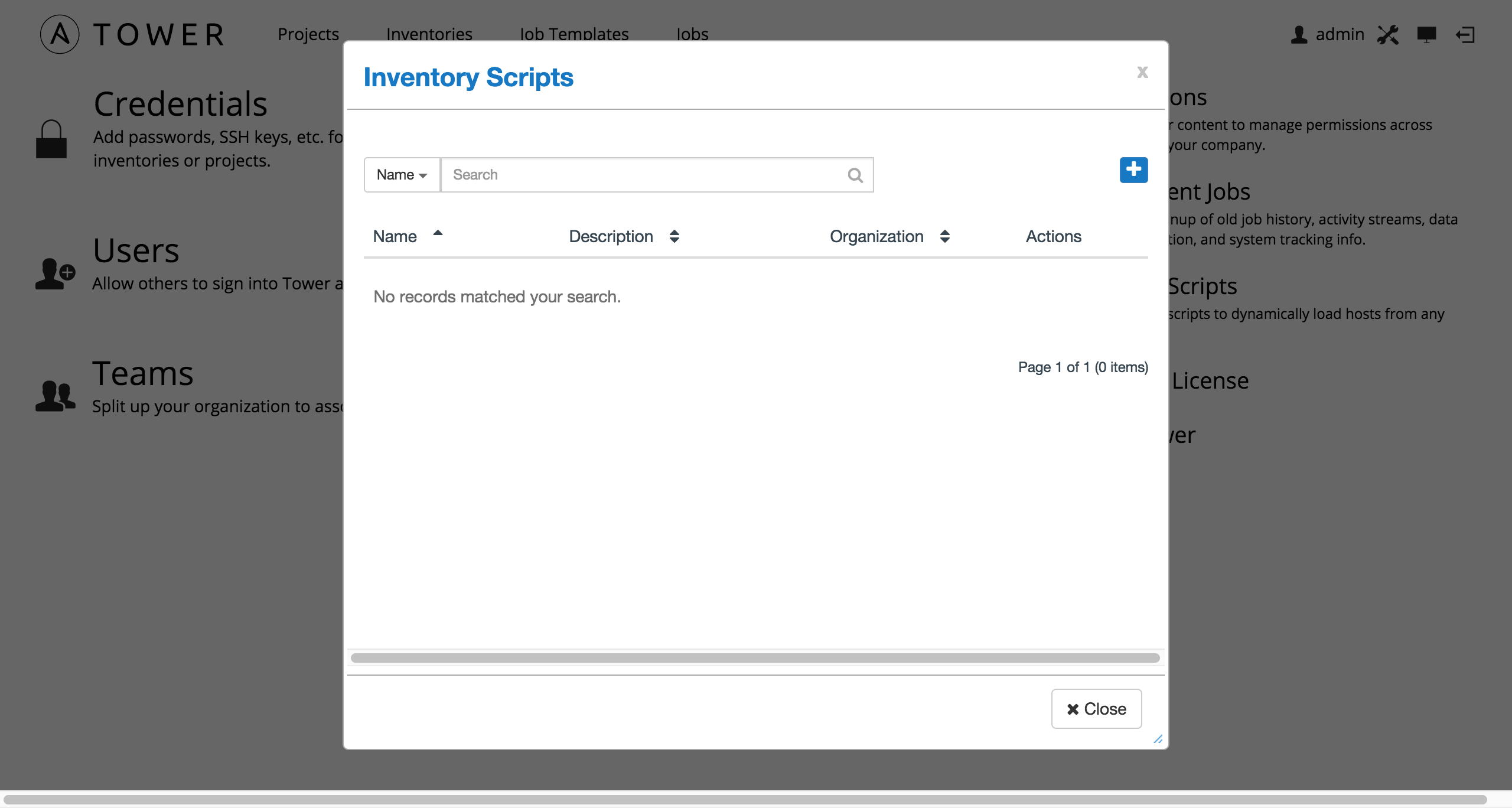
To add a new custom inventory script, click the  button.
button.
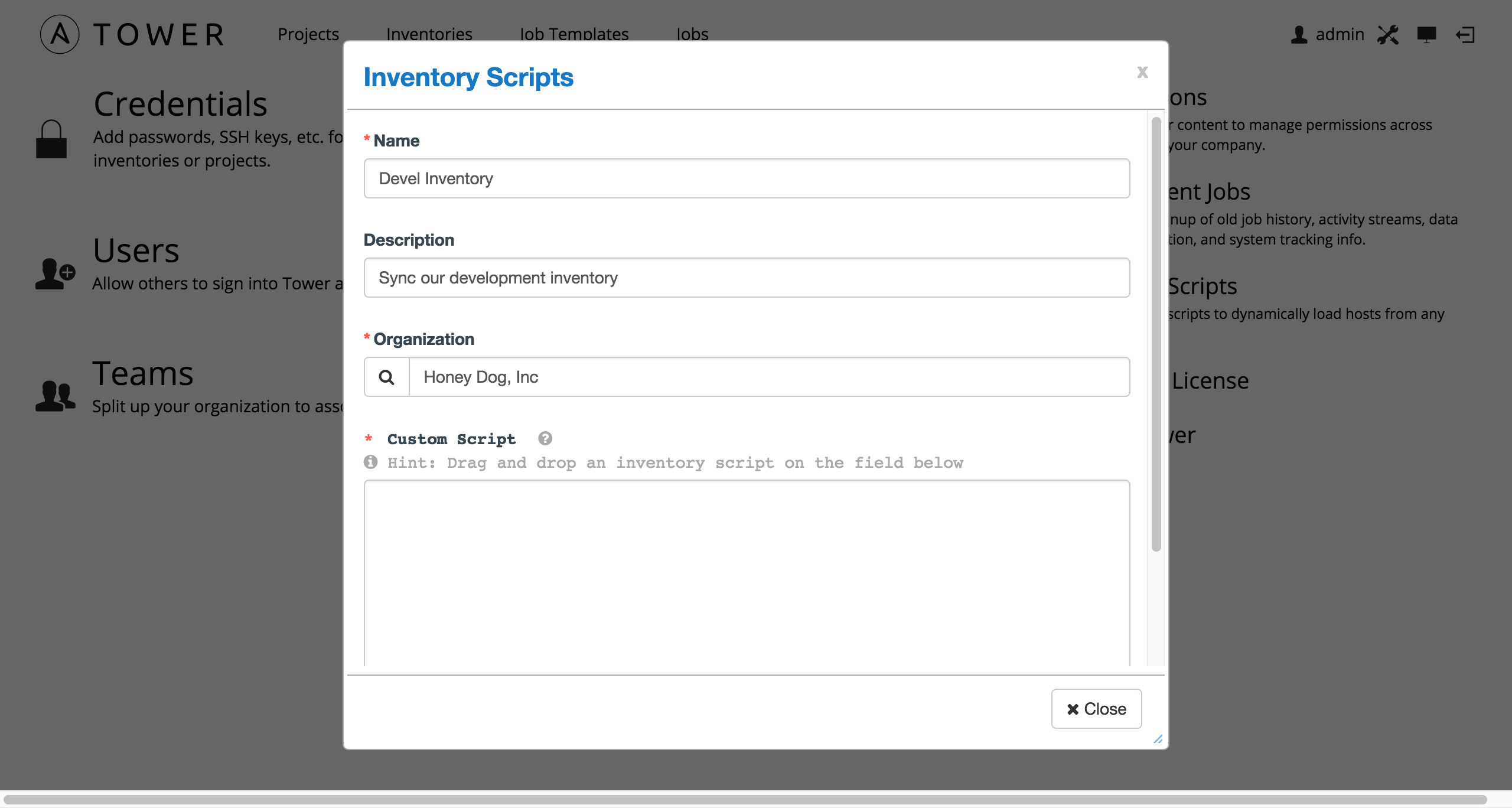
Enter the name for the script, plus an optional description. Then select the Organization that this script belongs to.
You can then either drag and drop a script on your local system into the Custom Script text box, or cut and paste the contents of the inventory script there.
3.1. Writing Inventory Scripts¶
You can write inventory scripts in any dynamic language that you have installed on the Tower machine (such as shell or python). They must start with a normal script shebang line such as #!/bin/bash or #!/usr/bin/python. They run as the awx user. The inventory script invokes with '--list' to list the inventory, which returns in a JSON hash/dictionary.
Generally, they connect to the network to retrieve the inventory from other sources. When enabling multi-tenancy security (refer to Security for details), the inventory script will not be able to access most of the Tower machine. If this access to the local Tower machine is necessary, configure it in /etc/tower/settings.py.
For more information on dynamic inventory scripts and how to write them, refer to the Intro to Dynamic Inventory and Developing Dynamic Inventory Sources sections of the Ansible documentation, or review the example dynamic inventory scripts on GitHub.